SQL Server uses identity columns to auto generate values, normally keys. When you create an identity column, it has a data type and that data type has a maximum number of values.
- BigInt 9,223,372,036,854,775,808
- Int 2,147,483,647
- SmallInt 32,767
- tinyint 255
What happens when you try to insert a value in an identity column that is greater than the maximum value? You get an error and a failed transaction. Lets do that
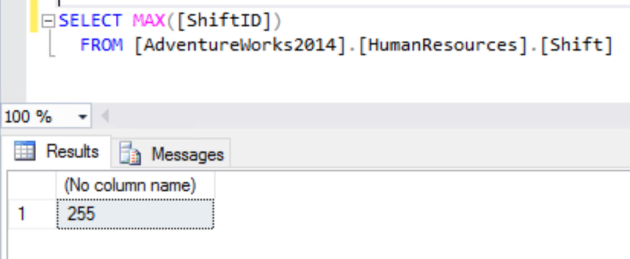
Using AdventureWorks, I know (I’ll show how in a minute) that the HumanResources.Shift column is a tinyint. So the highest value for the ShiftID column is 255.
If we run
USE AdventureWorks2014; GO INSERT INTO [HumanResources].[Shift] ([Name] ,[StartTime] ,[EndTime] ,[ModifiedDate]) VALUES ( 'Made Up SHift ' + CAST(NEWID() AS nvarchar(MAX)) ,DATEADD(hour,-4, GetDate()) ,'07:00:00.0000000' ,GetDate()) WAITFOR DELAY '00:00:00.050'; GO 252
So what happens if we try to add another row?
USE AdventureWorks2014; GO INSERT INTO [HumanResources].[Shift] ([Name] ,[StartTime] ,[EndTime] ,[ModifiedDate]) VALUES ( 'Made Up SHift ' + CAST(NEWID() AS nvarchar(MAX)) ,DATEADD(hour,-4, GetDate()) ,'07:00:00.0000000' ,GetDate()) GO
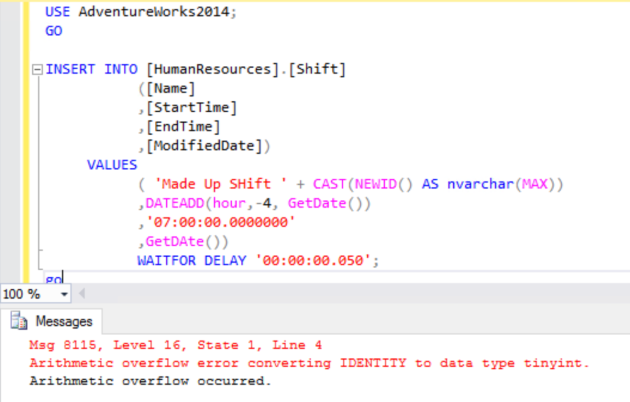
Msg 8115, Level 16, State 1, Line 4Arithmetic overflow error converting IDENTITY to data type tinyint.
Arithmetic overflow occurred.
USE AdventureWorks2014
GO
DELETE FROM HumanResources.Shift
WHERE ShiftId > 3
GO
DBCC CHECKIDENT ('HumanResources.Shift', RESEED, 3)
GOGet-Help Test-DbaIdentityUsage -ShowWindow
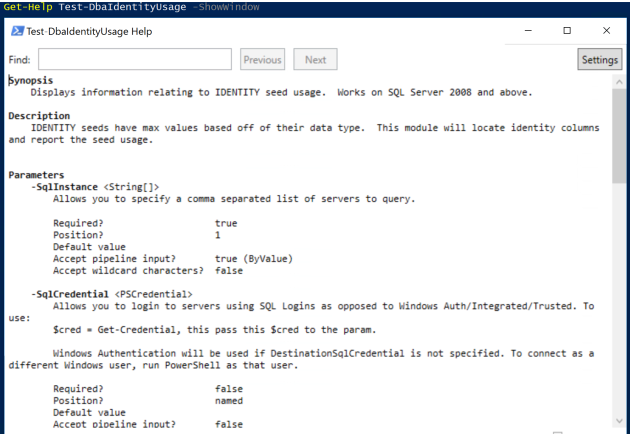
The command has a few parameters
- SqlInstance – One or many Instances
- SqlCredential – for SQL Authentication
- Databases – to filter for databases ( This is a dynamic parameter and doesn’t show in the Help)
- Threshold – define a minimum percentage for how full the identity column is
- NoSystemDB – to ignore the system databases
So we can run the command against one instance
Test-DbaIdentityUsage -SqlInstance sql2014ser12r2

This returns an object for each identity column in each database on the instance. The object has the following properties
ComputerName : SQL2014SER12R2
InstanceName : MSSQLSERVER
SqlInstance : SQL2014SER12R2
Database : AdventureWorks2014
Schema : HumanResources
Table : Shift
Column : ShiftID
SeedValue : 1
IncrementValue : 1
LastValue : 3
MaxNumberRows : 254
NumberOfUses : 3
PercentUsed : 1.18
We can use the objects returned from this command in a number of ways, this is one of the beauties of PowerShell that we can interact with numerous systems. I have blogged about some simple ways of doing this here but your only limit is your imagination.
I love to use Out-GridView as it enables quick and easy sorting of the returned data

The databases parameter is dynamic so it will prefill the names of the databases on the instance. This is what it looks like in VS Code

and in ISE

We can use the threshold parameter to only show results for the identity columns whose value is above a percent of the max value for the column. Lets fill the ShiftId column to above 90% and show this
USE AdventureWorks2014; GO INSERT INTO [HumanResources].[Shift] ([Name] ,[StartTime] ,[EndTime] ,[ModifiedDate]) VALUES ( 'Made Up SHift ' + CAST(NEWID() AS nvarchar(MAX)) ,DATEADD(hour,-4, GetDate()) ,'07:00:00.0000000' ,GetDAte()) WAITFOR DELAY '00:00:00.050'; GO 230
and now run
Test-DbaIdentityUsage -SqlInstance sql2014ser12r2 -Threshold 90

Don’t forget to use the cleanup script. You can pass a whole array of SQL instances to the command. We can pass an array of SQL servers to this command as well and check multiple servers at the same time. In this example, I am querying my Hyper-V server for all VMs with SQL in the name,except for my broken SQL2008 box ,that are running. Just to get some results I will set the threshold to 1
$SQLServers = (Get-VM -ComputerName beardnuc | Where-Object {$_.Name -like '*SQL*' -and $_.Name -ne 'SQL2008Ser2008' -and $_.State -eq 'Running'}).Name
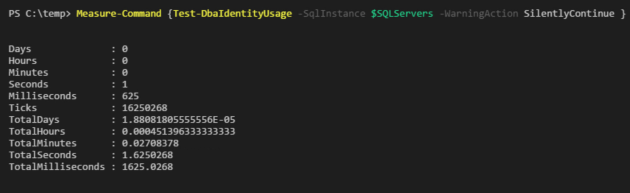
Test-DbaIdentityUsage -SqlInstance $SQLServers -Threshold 1 | Out-GridView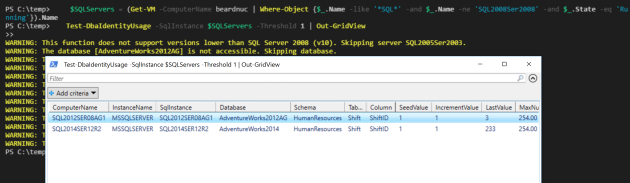
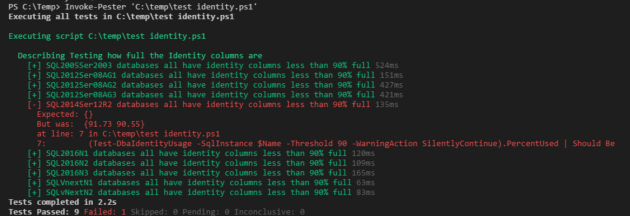
Describe "Testing how full the Identity columns are" {
$SQLServers = (Get-VM -ComputerName beardnuc | Where-Object {$_.Name -like '*SQL*' -and $_.Name -ne 'SQL2008Ser2008' -and $_.State -eq 'Running'}).Name
$testCases= @()
$SQLServers.ForEach{$testCases += @{Name = $_}}
It "<Name> databases all have identity columns less than 90% full" -TestCases $testCases {
Param($Name)
(Test-DbaIdentityUsage -SqlInstance $Name -Threshold 90 -WarningAction SilentlyContinue).PercentUsed | Should Be
}
}
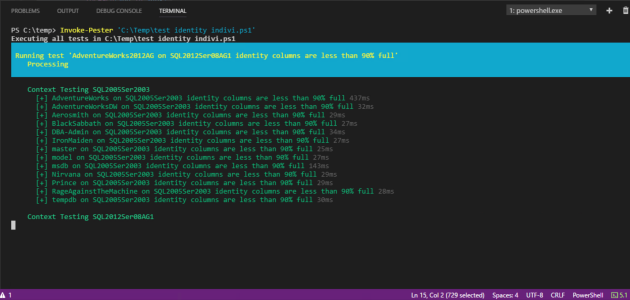
Describe "Testing how full the Identity columns are" {
$SQLServers = (Get-VM -ComputerName beardnuc | Where-Object {$_.Name -like '*SQL*' -and $_.Name -ne 'SQL2008Ser2008' -and $_.State -eq 'Running'}).Name
foreach($SQLServer in $SQLServers)
{
Context "Testing $SQLServer" {
$dbs = (Connect-DbaSqlServer -SqlServer $SQLServer).Databases.Name
foreach($db in $dbs)
{
It "$db on $SQLServer identity columns are less than 90% full" {
(Test-DbaIdentityUsage -SqlInstance $SQLServer -Databases $db -Threshold 90 -WarningAction SilentlyContinue).PercentUsed | Should Be
}
}
}
}
}
$SQLServers = (Get-VM -ComputerName beardnuc | Where-Object {$_.Name -like '*SQL*' -and $_.Name -ne 'SQL2008Ser2008' -and $_.State -eq 'Running'}).Name
foreach($SQLServer in $SQLServers)
{
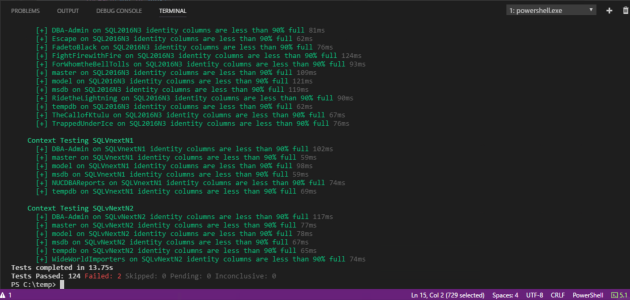
Describe "$SQLServer - Testing how full the Identity columns are" {
$dbs = (Connect-DbaSqlServer -SqlServer $SQLServer).Databases.Name
foreach($db in $dbs)
{
Context "Testing $db" {
$Tests = Test-DbaIdentityUsage -SqlInstance $SQLServer -Databases $db -WarningAction SilentlyContinue
foreach($test in $tests)
{
It "$($test.Column) identity column in $($Test.Table) is less than 90% full" {
$Test.PercentUsed | Should BeLessThan 90
}
}
}
}
}
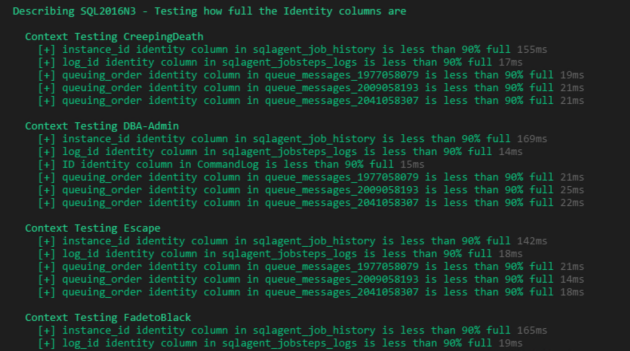
}
The other question that we have to answer these days is – Does it work with SQL on Linux? We will have to pass a SQL authentication credential and this time I will use Format-Table for the output
Test-DbaIdentityUsage -SqlInstance LinuxvNextCTP14 -SqlCredential (Get-Credential) | Format-Table

Happy Automating!
NOTE – The major 1.0 release of dbatools due in the summer 2017 may have breaking changes which will stop the above code from working. There are also new commands coming which may replace this command. This blog post was written using dbatools version 0.8.942 You can check your version using
Get-Module dbatools
and update it using an Administrator PowerShell session with
Update-Module dbatools
You may find that you get no output from Update-Module as you have the latest version. If you have not installed the module from the PowerShell Gallery using
Install-Module dbatools
Then you can use
Update-dbatools


