Trace Flags are a way to change the behavior of the SQL Server database engine. They are often used for diagnosing problems or opting in to or out of changes that could improve performance of certain aspects of your workload. New optimizations are often trialed in the database engine as part of a trace flag you that have to manually enable.
As far as I known Microsoft make no guarantee that a trace flag will be available from one version to the next, They also don’t have a definitive list of all the trace flags available in each version of SQL Server. A number of them get documented but there are also a number of undocumented trace flags that can be found on different sites via Google. These Trace Flags can have side effects and should always be tested before using them in production.
As an example of a use for a Trace Flag, in SQL Server 2012 they changed the way the unknown precision of numeric types from Oracle OLEDB connections are parsed causing numbers to be rounded differently over these connections. This particular change would have prevented upgrading an older SQL Server to 2012 or above as numeric types would suddenly be handled differently, enabling the undocumented trace flag 7314 can set it back to the older behavior.
When you enable a trace flags it’s enabled only enabled until the SQL Server restarts. If you want a trace flag to persist restarts then you need to pass some optional startup arguments to the SQL Server service so when it starts it turns them back on again.
Enabling/Disabling a Trace Flag In TSQL
Trace Flags can be enabled for either the current session or globally.
To enabled a trace flag for the current session you need to call DBCC TRACEON and pass in the number of the trace flag…
DBCC TRACEON(1205)If you want to enable a trace flag globally for all sessions then pass in a second argument of -1…
DBCC TRACEON(1205,-1)To disable we use DBCC TRACEOFF, as with enabling a trace flag when disabling you need to specify if you want to disable it for the current session or globally with -1 being global…
/*Disable for session*/
DBCC TRACEOFF(1205)
/*Disable globally*/
DBCC TRACEOFF(1205,-1) Enabling Trace Flags On Instance Start
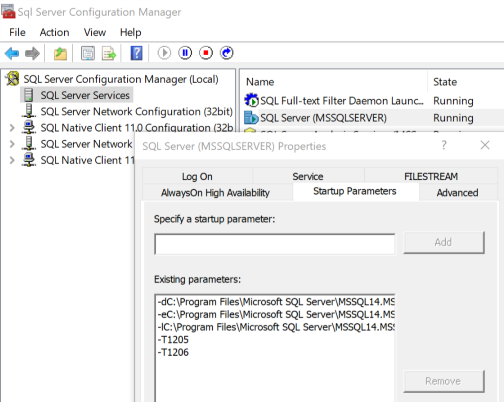
If you want flags to persist server restarts then you need to add them as startup parameters. To do this you need to go into SQL Server Configuration Manager and follow these steps
- Click SQL Server Services
- Go to the properties of the SQL Server instance on the right
- Click the startup parameters tab
- For each flag you want to enable add a new startup parameter of -T### where ### is the trace flag number. For example -T1205
Checking What Trace Flags Are Enabled
To list enabled trace flags you’ll want to use DBCC TRACESTATUS, as with the above examples we can list current session only flags by passing no arguments or global flags by passing in -1…
/*List session flags*/
DBCC TRACESTATUS()
/*List global flags*/
DBCC TRACESTATUS(-1)

