No no, I didn’t say temporary, but temporal! SQL Server 2016 introduces a great new feature called Temporal Tables. Or in other words, system-versioned tables. We’ll see what catches on. In a gist, such a table keeps track of the history of its rows by the use of some audit columns (start and end date) and a history table. Sounds a bit like the love child of Change Data Capture and a Type 2 dimension.
Anyway, I was testing this feature a bit (more specifically if they supported computed columns as promised in CTP 2.1) and I created a temporal table with the following query:
CREATE TABLE dbo.TestTemporal (ID int primary key ,A int ,B int ,C AS A * B ,SysStartTime datetime2 GENERATED ALWAYS AS ROW START NOT NULL ,SysEndTime datetime2 GENERATED ALWAYS AS ROW END NOT NULL ,PERIOD FOR SYSTEM_TIME (SysStartTime,SysEndTime)) WITH(SYSTEM_VERSIONING = ON);
This code only works in CTP2.1, not in earlier versions of SQL 2016 because of the computed column specification.
Anyway, of course I forgot to set my database so this table was created in the master database. I wanted to drop it, but I was greeted with this lovely message:
Even the Delete action was missing from the table’s context menu.
A quick look on the MSDN page Temporal Tables teaches us that dropping a system-versioned table is a disallowed Alter Schema operation. No luck there. The answer came, as usual, through Twitter:
@Ko_Ver did you try to remove temporal setting before dropping it?
— Janos Berke (@JanosBerke) June 29, 2015
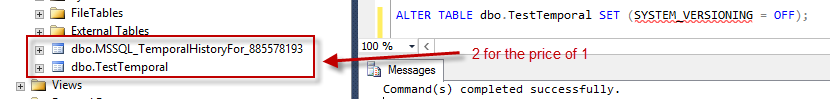
Turning the system-versioning off and dropping the table is the answer to our question (and to about any schema operation you want to do on a system-versioned table). If we execute such an ALTER TABLE script, we get the following:
The temporal table is reduced to a normal table, which means it can be dropped as a normal table. But the history table is kept as well. This means you can always re-enable system-versioning if you want to.
The name of the history table is dbo.MSSQL_TemporalHistoryFor_xxx, where xxx is the object id of the main table. Something to keep in mind if you want to automate scripts. Or just specify a friendly name when enabling system-versioning.