[ID] Int identity(1,1) PRIMARY KEY NONCLUSTERED HASH WITH (BUCKET_COUNT = 1024) NOT NULL ,
[Data] uniqueidentifier DEFAULT newsequentialid() ,
[dt] datetime NOT NULL ) WITH (MEMORY_OPTIMIZED = ON, DURABILITY = SCHEMA_AND_DATA);
* FROM
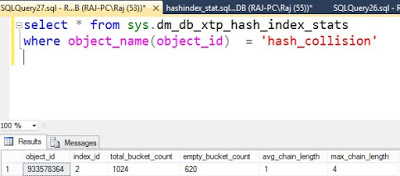
- "Total Bucket count" indicates the number of buckets in the hash index which is fixed.
- "Empty Bucket count" indicates the number of buckets that are empty. In this case, close to 50% are empty as we have inserted only 500 rows.
- "Average Chain Length" indicates average length of a hash chain. In other words, average number of hops one may need to take to find a row.
select * FROM sys.dm_db_xtp_hash_index_stats WHERE object_name(object_id) = 'hash_collision'
dm_db_xtp_hash_index_stats indicates that 80% of the buckets are full but the average hash chain length is still at 1 as there are still a few empty hash buckets.
Step 3: Add 9000 rows
Let us add few more thousands - say 9000 rows. Now table contains 10,000 rows but only 1024 hash buckets
Insert into hash_collision(dt) select getdate()
go 9000
SELECT * FROM sys.dm_db_xtp_hash_index_stats
WHERE object_name(object_id) = 'hash_collision'
Notice a sharp increase in "Average Chain Length" as there more values than the number of buckets. The number of empty buckets is obviously zero.
So does longer hash chain affect the performance? Longer hash chains cause reads or the index scan to be slower. So, it is important to pick the hash bucket count carefully. General recommendation is at least 2 times the number of distinct values in the table. Also, it is always better to over size the hash bucket count instead of under sizing it.