I was reading SqlServerCentral.com Articles Requested forum and saw this request.
Looking for an article that takes data from an XML column in a table and exports each field as a separate document.
While the request did indicate a PoSH or SSIS method, I wanted to give it a try using T-SQL. Lets look at how I managed it.
The Setup
To get started, I do some requisite cleanup, declare a few variables and create a simple table to hold our XML column that we will be exporting.
USE DBA;
SET NOCOUNT ON;
declare @x xml
, @cmd nvarchar(255)
, @name varchar(100)
, @OutputPath varchar(100) = 'C:\temp\'
/*** Basic CleanUp ***/IF OBJECT_ID('DBA.dbo.MetaData') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE dbo.MetaData
IF OBJECT_ID('tempdb.dbo.#Export') IS NOT NULL
DROP TABLE #Export
/*** Create Table ***/create table MetaData (
id int IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
documentName varchar(100) NOT NULL,
document XML not NULL
)For data, lets query some of the system tables. In this case I’m going to create one XML document for Databases, Users, and Jobs.
/*** Fill our table ***/select @x = (
select
name,
create_date,
compatibility_level,
collation_name
from sys.databases [database]
where
name in ('master','model','tempdb','msdb')
for xml auto, root('databases'), elements
)
insert into MetaData (documentName, document) values ('Databases', @x )
select @x = (
select
name,
type_desc,
create_date
from sys.server_principals
where principal_id < 258
for xml auto, root('users'), elements
)
insert into MetaData (documentName, document) values ('Users', @x )
select @x = (
select
name,
description,
date_created
from msdb.dbo.sysjobs [job]
where enabled=1
for xml auto, root('jobs'), elements
)
insert into MetaData (documentName, document) values ('Jobs', @x )
And finally, we can use BCP to get our columns to disk:
CREATE PROCEDURE sp_DocumentToDisk @documentName varchar(20), @Location varchar(200) AS BEGIN declare @cmd varchar(2000) set @cmd = 'bcp "SELECT document FROM DBA.dbo.MetaData where documentName=''' + @documentName + '''" queryout ' + @Location + '\' + @documentName +'.xml -c -T' EXEC xp_cmdshell @cmd END
Using this procedure we can pass in a document name, and the location we wish to save the XML file and get our results by calling the procedure like this:
exec sp_DocumentToDisk 'Databases', 'c:\temp' exec sp_DocumentToDisk 'Users', 'c:\temp' exec sp_DocumentToDisk 'Jobs', 'c:\temp'
Which results in three new files sitting in our C:\Temp directory:
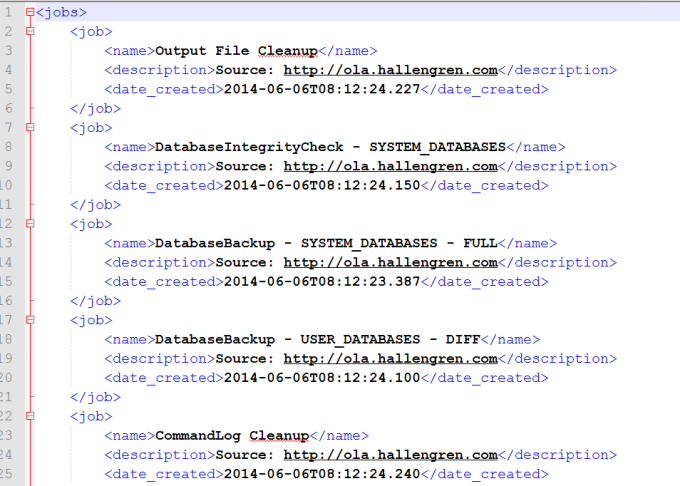
The contents of those files are simply the XML we have stored in the XML typed document column.
Things to Think About
This approach is demonstrating the basic mechanics of how it would work, but there are a few things to keep in mind. Many DBAs will restrict xp_cmdshell, as they rightly should, as it can be very dangerous in the wrong hands, but with proper precautions and monitoring, it is a valid tool in your tool belt. One final thing to think about is permissions. When xp_cmdshell is run, it runs as the SQL Server Service Account, unless configured more precisely with sp_xp_cmdshell_proxy for instance. Which ever account that is being used will need permissions to write to the @Location you provide.
Comments, Suggestions
This is my approach using T-SQL, I’d love to hear feedback on my approach or holes in where my approach might be wrong. Thanks for stopping by.


