Have you ever wondered whether it is possible to restrict installation of the Power BI Gateways (GW) in your tenant? If so, read along…
The first question that probably comes up to your mind might be why would you like to restrict it…Hmm, that is a good one. I guess that there are several reasons to limit this kind of activity, for instance, if you want to:
- follow internal data governance & security policies
- privilege only some team/bunch of admins to do the installations
- control who will be able to add data sources to existing/newly installed GWs
- control which on-premise data sources will be available in Power BI Service
- control who can consume the data sources
- control who can restore/migrate GWs
- control who can create GW clusters
- control who can add GW to GW clusters
…and maybe there are some other as well. Now when we are aware about the purpose, how is it possible to restrict it?
It is easy! In accordance with the documentation, you must be either Azure AD Global Admin, Power BI Service admin, or Gateway admin (honestly, I am not familiar with the last role and have not found much about it in MS Docs). Then you can head to Power Platform admin center and specifically to Data (Preview) blade section.
Data (Preview) provides a place for managing all active and inactive Power BI GWs. You can view, edit, and remove both Standard as well as Personal GWs. In comparison to Power Platform admin center the “Manage Gateway” feature in Power BI Service displays only the GWs you have installed & configured, or you have been assigned as co-administrator by someone else (even though you are a Power BI admin).
Ok, back to the topic… over there in the Data (Preview) there is a toggle button (Tenant administration) that gives you a chance to hit “Manage gateway installers”, see the snip below.
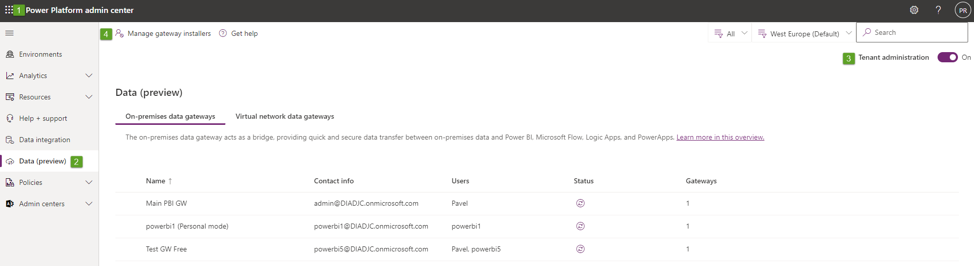
Once you open the settings pane you can force “Restrict users in your organization from installing gateways” and then you can specify which users will be privileged to do the GWs installations. Those ones will be able to seamlessly install the GWs and configure them in Power BI Service. Users that are not designated will bump into installation failures as displayed below.
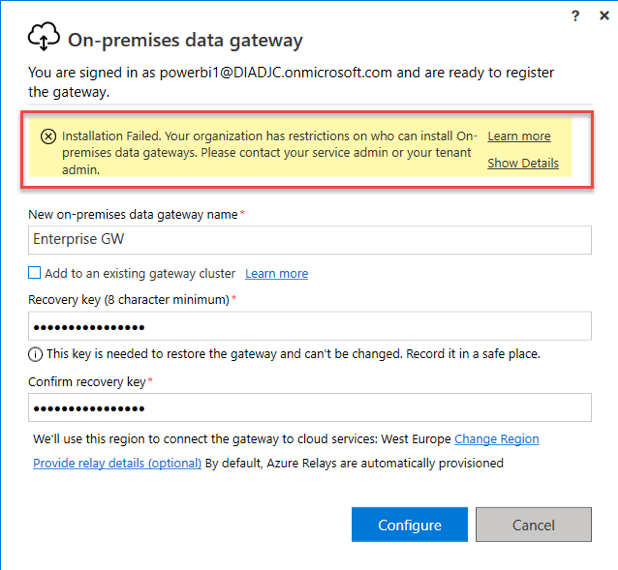
Bear in mind that this restriction applies only to Standard (formerly Enterprise) Power BI GW installations. Installations of Personal Power BI GW will still be possible for the non-privileged users (unless you use the restriction feature via PowerShell Cmdlets, check out the great video from Guy in a Cube). However, those GWs can’t be shared and have some other limitations that exclude any collaboration on top of them, see docs if you are unfamiliar about the discrepancies between Standard and Personal GW.
Pretty useful feature, right? If you are tenant admin of Power BI in your organization and don’t have this setting implemented yet I think you should put it in first place on your to-do list! 
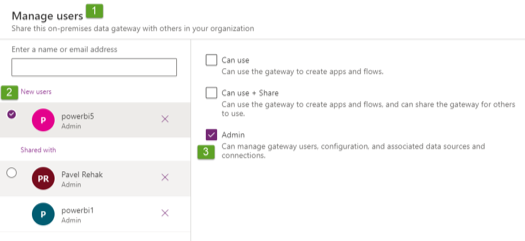
I have one more interesting thing for you. I was not sure whether it is mandatory to have a Power BI Pro license to install Standard Power BI GW. What would you guess? Initially, I thought that you must have a Pro license to install the Standard GW. Hence, I have tried to install Standard GW with a Free license just to double-check my assumption. And I have found out I was wrong. Standard GW can be installed by a user with a Power BI Free license and then some user with Power BI Pro license can be added as a co-administrator of that GW or as a user of some data source (see below how this is done).
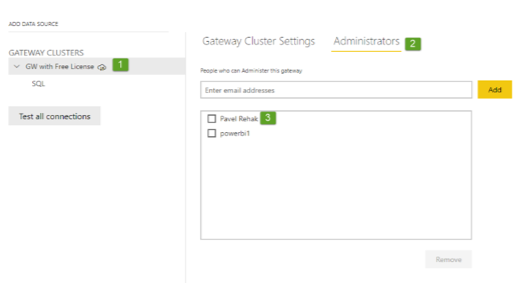
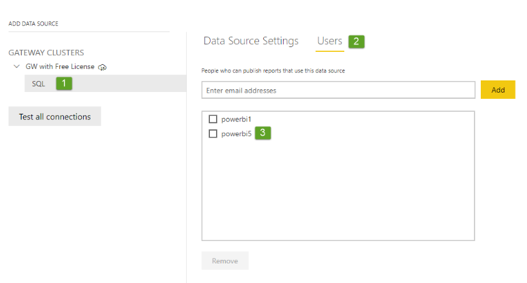
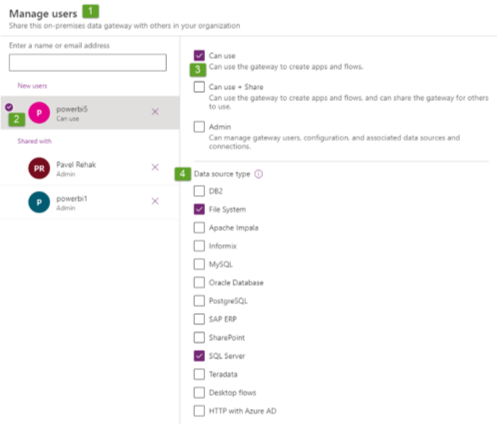
Adding the co-administrators of the GWs is possible even from the Power Platform admin center (see below), but you can’t add the user to some specific data source, you can just limit what types of data sources he will be able to use (in my case File System & SQL Server, see below).