Introduction
There
are lots of articles about how to do auditing, but there are few discussions
about how to use the auditing results in a real time environment, for example,
an employee salary table has a delete operation during non-working hours, a
responsible DBA should be notified for this unusual operation asap.
In this
article, I propose a new security mechanism based on the auditing trace of SQL
Server 2000. There are two distinct advantages to this security model:
- Any
monitored events can be reported to the concerned parties as soon as
possible.
- All
responding actions can be centered in a same place.
Security
Mechanism Description
There
are four major components in building this security model
- An
auditing trace is established to monitor any concerned events
- A
job is setup to export the trace file to a trace table every fixed period
- An
alert is created with notification functions set
- A
trigger on the trace table will fire out notifications (email, pager) to
concerned people by raising a low severity error.
The
process flow is as follows:
An
auditing trace will record any concerned events to a trace file, and the job
will from time to time import the trace file to a table, on which there is a
trigger. The trigger will detect whether there is any specific events occurring
to specific targets, if yes, raise error, which trigger the alert to be fired
and the necessary notification will be issued as a result.
Implementation details
- Creating
an auditing trace
a)
Start the profiler, create a trace that can monitor your interested
events, as shown in Fig 1.
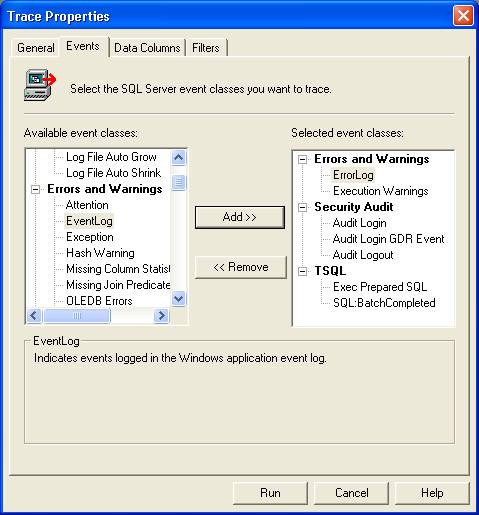
Fig 1: Create a trace for your interested events
Also it
is better to filter out any events generated by SQL Alert engine as shown in Fig
2.
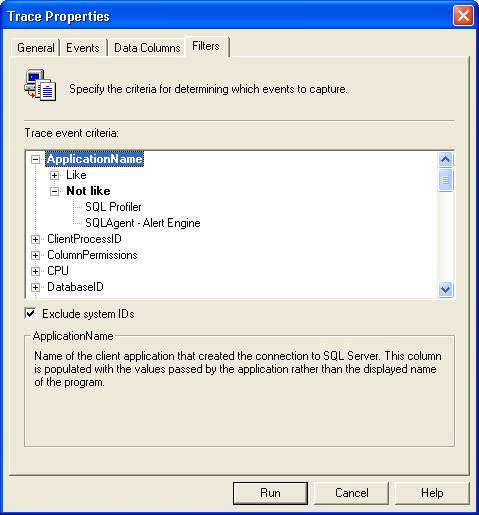
Fig 2:
Filter out events generated by SQL Agent
b)
Go to menu File -> Script trace -> SQL Server 2000, you will save
an sql file. It is similar to the following script:
/****************************************************/
/*
Created by: SQL Profiler
*/
/*
Date: 02/28/2004 11:35:51 AM
*/
/****************************************************/
create
procedure usp_MyTrace as /* this line is added by myself to create a stored proc
*/
--
Create a Queue
declare
@rc int
declare
@TraceID int
declare
@maxfilesize bigint
set
@maxfilesize = 5
--
Please replace the text InsertFileNameHere, with an appropriate
--
filename prefixed by a path, e.g., c:\MyFolder\MyTrace. The .trc extension
--
will be appended to the filename automatically. If you are writing from
--
remote server to local drive, please use UNC path and make sure server has
--
write access to your network share
exec
@rc = sp_trace_create @TraceID output, 0, N'InsertFileNameHere', @maxfilesize,
NULL
--
note: change “InsertFileNameHere” to your local file with full path, e.g.
“c:\test.trc”
if
(@rc != 0) goto error
--
Client side File and Table cannot be scripted
--
Set the events
declare
@on bit
set
@on = 1
exec
sp_trace_setevent @TraceID, 12, 1, @on
exec
sp_trace_setevent @TraceID, 12, 6, @on
…………………………..
………………………….
error:
select
ErrorCode=@rc
finish:
go
Open
this SQL Profiler created file and add a line of code (create
proc usp_MyTrace as ) in the beginning of the code, so
you will get a stored procedure.
After
the procedure is created, generate the stored procedure in master
database if you want to use sp_procoption to make it run automatically every
time SQL Server is started.
Exec sp_procoption ‘usp_MyTrace’, ‘startup’, true
Otherwise, you can generate the stored proc in your own database and use a job
to schedule this procedure execution.
c)
Create a table with similar columns in the trace, plus an identity column (can
be omitted, but I prefer to have it for clarity reason only)
Create
table TraceTable
(
RowID int identity primary key, TextData nvarchar(4096), Reads int, Writes int,
StartTime datetime, LoginName sysname, NTUserName sysname)
- Creating
a job
The
job contains only one sql statement
insert
into TraceTale (textdata, Reads, Writes, StartTime, LoginName, NTUserName)
select
left(textdata, 4096), Reads, Writes, StartTime, LoginName, NTUserName
from ::fn_trace_gettable('c:\test.trc', default)
- Creating
an alert
In
my case, I created an alert with an error number 50005 and made the notification
responding to this alert. The notification is to send email to an operator. (You
can page the operator too if your system supports the function.)
- Creating
a trigger
In
my case, I try to detect whether there is a read statement to a specific table
create
trigger tr_Read_ on xx
for
insert
as
begin
if update (TextData)
begin
if exists (select * from inserted
where TextData
like ‘%select%EmployeeSalary%’)
raiserror (50005, 10, 1)
end
end
Summary
In this
paper, a new auditing solution is proposed in an environment that quick response
is critical. The solution design is based on a combined use of SQL Server’s
various components, such as trace file, trigger, job and alerts. It has an
advantage when used in monitoring multiple database environments so a DBA can
have a centered place to monitor all those sensitive operations. It can be
considered as a mimic implementation of “select” trigger.

