SQL Server 6.5 uses three security modes:
- Standard
- Integrated
- Mixed
The security mode is selected during SQL Server 6.5 installation and can
be modified at any time.
To change the security modes, you can do the following:
Click Start, Programs, Microsoft SQL Server 6.5 and click
SQL Enterprise Manager to run SQL Enterprise Manager from the
Microsoft SQL Server 6.5 program group.
Select the server you want to work with, then from the Server menu
select SQL Server, Configure and choose the Security Options page.
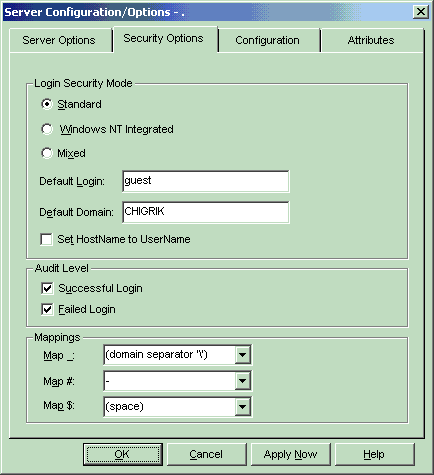
Set SQL Server 6.5 security mode.
Standard Security
This security mode is used by default. In this case, SQL Server manages
its own login validation process for all connections, i.e. SQL Server
is wholly responsible for authenticating a user and for enforcing
password and login restrictions.
Integrated Security
When it is used, then Windows NT is responsible for managing user
connections through its Access Control List (ACL). So the advantage
of using Windows NT Integrated Security mode is single-password
access to all resources on a Windows NT domain and password aging
and encryption across the network.
With Integrated Security, only Multi-Protocol and Named Pipes clients
are supported, and only trusted connections are allowed into SQL Server
(trusted connections are only available via the Multi-Protocol or via
Named Pipes).
Mixed Security
Mixed Security is a combination of the standard and integrated security.
In this case, when a user connects to a SQL Server, then SQL Server
checks is it a trusted connection or not (checks is the login name
matches the user's network username, or if the login name is null).
If it is a trusted connection, then SQL Server uses Windows NT
authentication, if it is not a trusted connection then SQL Server
uses Standard Security (i.e. tried to find the same SQL Server login
name and password, as user has passed).
This security mode is usually used when there are many different clients
connected to SQL Server, and one of them use trusted connections and
other use standard security (SQL Server login and password).

