One of the new features in SQL2016 is the ability to distribute availability groups across clusters. This solution makes high availability and disaster recovery geographically dispersed.
Distributed Availability groups allows you to associate availability groups on two different Windows Server Failover Clusters.
Pre-Requisites for this Example:
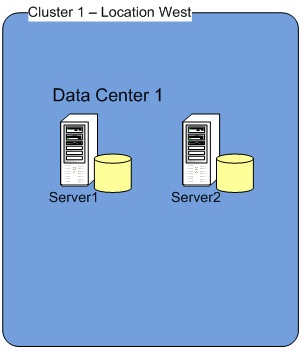
Cluster 1 – Location West
| Server Name | SQL Server 2016 | Subnet |
| Server1 | Standalone Instance | A |
| Server2 | Standalone Instance | A |
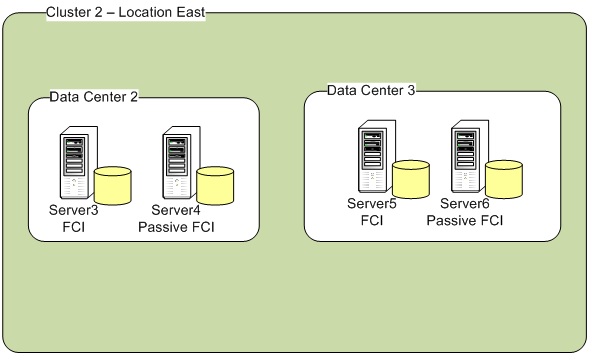
Cluster 2 – Location East
Server Name | SQL Server 2016 | Subnet |
Server3 | SQL FCI | B |
Server4 | SQL FCI | B |
Server5 | SQL FCI | C |
Server6 | SQL FCI | C |
This example covers a basic set up of the distributed availability group. Here we will create an Availability Group on Cluster 1 and create an Availability Group on Cluster 2. Then we will create listeners. Then finally create the distributed availability group. In our testing scenario we did not use Automatic Seeding.
Create AG_1 on Cluster 1. This will be the Primary for all of the replicas in the Distributed Availability Group
CREATE AVAILABILITY GROUP AG_1
FOR DATABASE AdventureWorks
REPLICA ON N'Server1\Instance1' WITH (ENDPOINT_URL = N'TCP://Server1.com:5022',
FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL,
AVAILABILITY_MODE = ASYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
BACKUP_PRIORITY = 50,
SECONDARY_(ALLOW_CONNECTIONS = ALL)
),
N'Server2\Instance2' WITH (ENDPOINT_URL = N'TCP://Server2.com:5022',
FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL,
AVAILABILITY_MODE = AYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
BACKUP_PRIORITY = 50,
SECONDARY_(ALLOW_CONNECTIONS = ALL)
)
GO
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP AG_1 JOIN
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP AG_1 GRANT CREATE ANY DATABASE
There are other options for the AG such as load balancing across replicas using the READ_ONLY_ROUTING_LIST which will be discussed in another article.
Configure the listener for the standalone instances
USE [master] GO ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [AG_1] ADD LISTENER N'SQL-01' ( WITH IP ((N'11.222.33.101', N'255.255.252.0') ) , PORT=44441); GO
Now let’s setup the Secondary Cluster, Cluster 2.
CREATE AVAILABILITY GROUP AG_2
FOR
REPLICA ON N'Server3\Instance1' WITH (ENDPOINT_URL = N'TCP://S11100008111:5022',
FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL,
AVAILABILITY_MODE = AYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
BACKUP_PRIORITY = 50,
SECONDARY_(ALLOW_CONNECTIONS = ALL)
),
N'Server5\Instance2' WITH (ENDPOINT_URL = N'TCP://S11100006155:5022',
FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL,
AVAILABILITY_MODE = ASYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
BACKUP_PRIORITY = 50,
SECONDARY_(ALLOW_CONNECTIONS = ALL)
)
GO
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP AG_2 JOIN
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP AG_2 GRANT CREATE ANY DATABASE
Configure the listeners for the FCIs
USE [master] GO ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP AG_2 ADD LISTENER N'S11100008115' ( WITH IP ((N'11.222.555.40', N'255.255.555.0'), (N'11.333.666.41', N'255.255.666.0') ) , PORT=44445); GO
Now we will join Cluster 1 AG_1 to Cluster 2 AG_2. When using listeners, use the listener name for the standalone instance and use the SQLVNN for FCIs when creating and joining the distributed availability group.
On Cluster 1 (Primary), run this:
CREATE AVAILABILITY GROUP [DAGisAwesome] WITH (DISTRIBUTED) AVAILABILITY GROUP ON 'AG_1' WITH ( LISTENER_URL = 'tcp://SQL-01:5022', --Use listener name when there is a standalone AVAILABILITY_MODE = ASYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT, FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL ), 'AG_2' WITH ( LISTENER_URL = 'tcp://S11100008111:5022', --Use SQLVNN not listener name when an FCI AVAILABILITY_MODE = ASYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT, FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL ); GO
On Cluster 2 (Secondary), run this:
ALTER AVAILABILITY GROUP [DAGisAwesome]
JOIN
AVAILABILITY GROUP ON
'AG_1' WITH
(
LISTENER_URL = 'tcp:// SQL-01:5022', --Use listener name when there is a standalone
AVAILABILITY_MODE = ASYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL
),
'AG_2' WITH
(
LISTENER_URL = 'tcp://S11100008111:5022', --Use SQLVNN not listener name when an FCI
AVAILABILITY_MODE = ASYNCHRONOUS_COMMIT,
FAILOVER_MODE = MANUAL
);
--Begin replication
ALTER DATABASE DBforTest SET HADR AVAILABILITY GROUP = AG_2
To verify successful connection with all replicas
select r.replica_server_name, r.endpoint_url,
rs.connected_state_desc, rs.last_connect_error_description,
rs.last_connect_error_number, rs.last_connect_error_timestamp
from sys.dm_hadr_availability_replica_states rs
inner join sys.availability_replicas r
on rs.replica_id=r.replica_id
From Server3:
replica_server_name | endpoint_url | connected_state_desc | last_connect_error_description |
Server3\Instance1 | TCP://111100008111:5022 | CONNECTED | NULL |
Server5\Instance2 | TCP://111100006155:5022 | CONNECTED | NULL |
AG_1 | tcp://SQL-01:5022 | CONNECTED | NULL |
AG_2 | tcp://111100008111:5022 | CONNECTED | NULL |
From Server1:
replica_server_name | endpoint_url | connected_state_desc | last_connect_error_description |
Server1\Instance1 | TCP://Server1.com:5022 | CONNECTED | NULL |
Server2\Instance2 | TCP://Server2.com:5022 | CONNECTED | NULL |
AG_1 | tcp://SQL-01:5022 | CONNECTED | NULL |
AG_2 | tcp://111100008111:5022 | CONNECTED | NULL |
If you are having trouble getting to a connected state, possible issues could be the user does not have sysadmin rights on instances, problem with database file locations, connection to other cluster, firewall issues.





