Last weeks article, "Configuration of STARSQL 3.0" showed you how to prepare the StarSQL driver
for SQL Server to access DB2. You can also use the OLE DB provider for DB2 that ships with Host Integration Services (formally known as SNA server). This week, we build on that knowledge and have the assumption that your StarSQL ODBC driver has
already been configured. We will dig a little deeper into configuring SQL Server's DTS (Data Transformation Services) to import
DB2 data and schemas.
A major consideration we must review is the datatypes of your DB2 data. You will need
to check the datatypes on DB2 and SQL Server to make sure that they will
support each other. The chart below covers covers the supportibilty of the datatypes (see books online for more information).
| SQL Server data type | IBM DB2 AS400 ODBC | IBM DB2 MVS ODBC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| binary(n) | L | S | |||
| bit | S | S | |||
| char(n) | S | S | |||
| datetime | S** | S** | |||
| decimal | S | S | |||
| float | S | L | |||
| image | N | N | |||
| int | S | S | |||
| money | S | S | |||
| nchar(n) | S | S | |||
| ntext | N | N | |||
| numeric | S | S | |||
| nvarchar(n) | S | S | |||
| real | S | S | |||
| smalldatetime | S | S | |||
| smallint | S | S | |||
| smallmoney | S | S | |||
| text | S | N | |||
| timestamp | S | S | |||
| tinyint | S | S | |||
| uniqueidentifier | S | S | |||
| varbinary(n) | S | S | |||
| varchar(n) | S | S | |||
| S = supported | L = limited support | N = not supported | |||
| S** See DTS Data Conversion and Transformation Considerations | |||||
- Begin the import by loading Import and Export Data in your SQL Server program group.
This is also accessible in MMC (Microsoft Management Console) under tools, Data Transformation Services, and Import Data
- Select a source server (see figure 1). I use StarSQL as my ODBC source to DB2 in this example. Select you
data source name for the User/System DSN Name. For the Username and Password option, make sure you select
your ID and password on the DB2 system for which the ODBC is configured for.
- Select the destination server and database name you'd like to export the data to (see figure 2).
- Check the tables you'd wish to import from the destination DB2 server. (HINT : If you are seeing any tables
here, then your connection to DB2 works and you've gotten the hard party working!).
- If you click to the right of any table, under the transform column you will get a column mapping screen (see figure 4).
This gives you the flexiblity to customize the desination tables. You can also turn on here identity inserting, which will keep
the integrety of your identity fields during an insert. If this import will be a repetitive task, then you may want to drop and recreate
the table if doing a complete refresh of the tables.
- You may want to modify the schema of the table that will be created on your SQL Server DBMS. You can do this by clicking Edit SQL (see figure 5) and making
the necessary changes. Generally it is not a good idea to change the SQL Server defaults during the initial loads. I've found SQL Server to have a pretty good native system for making schema creations.
- Also in the Column Mappings screen is the Transformations tab (see figure 7). This tab gives you the option
of adding some scripting business logic into the import of your DB2 data. You can by default use Javascript or ActiveX. You can also click on the browse icon to install
a custom scripting language, such as Pearl. I would advice against you doing this however, due to the native ActiveX scripting runs much faster. I will go into this option in more detail in a later article.
- After completetion of the transform section, the wizard will ask you if you'd like to save the package and run immediatly or schedule if for a later run.
Most DB2 databases can be extremely large in size, so it may be better if you schedule the DTS package to run later during an off peak hour. If you also plan to
repeat the importing process or you are in development, you can save time by saving the DTS package. The repository provides a useful tool for viewing metadata on the DTS package; the only
drawback being that it is slower loading and more I/O intensive.
- Your task will then execute. You may notice in the above DTS package running (figure 8) the error message in the drop table statement.
This is due to my selection to create the database and drop the database in the transformation section (see figure 4). In other words, SQL Server is issuing a drop command on a table that does not exist yet.
- You can later view the package and execute it again in the Data Transformation Services section of Enterprise Manager. Double Click on the package name (if you saved it), and the generic package you created will come up for edit (see figure 8).
We will go into much further detail about DTS in a later article. Again, feel free to email me if you have any questions. Microsoft will support this also if you are using StarSQL as a driver.
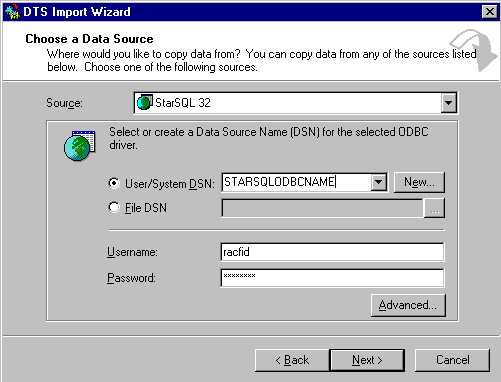
FIGURE 1
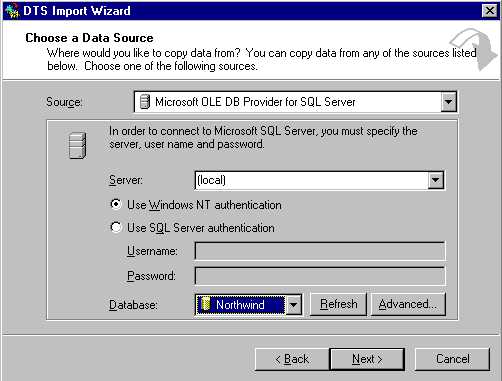
FIGURE 2
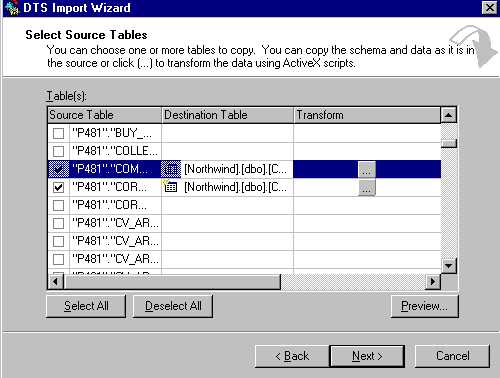
FIGURE 3
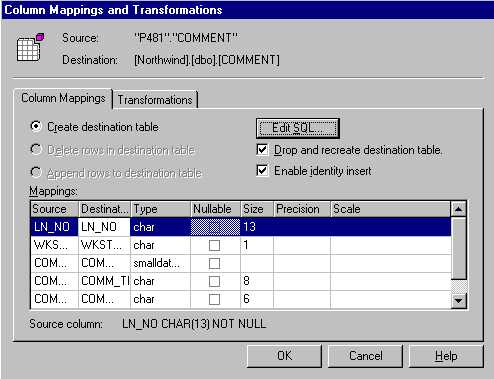
FIGURE 4
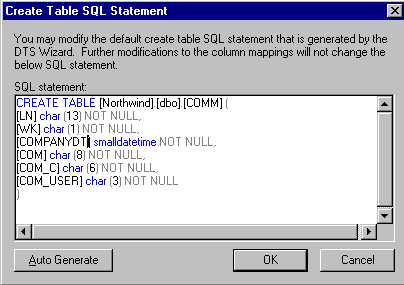
FIGURE 5
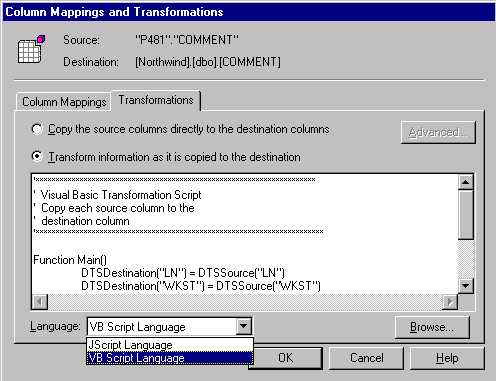
FIGURE 6
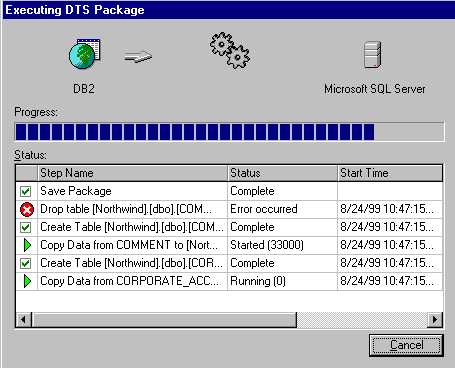
FIGURE 7
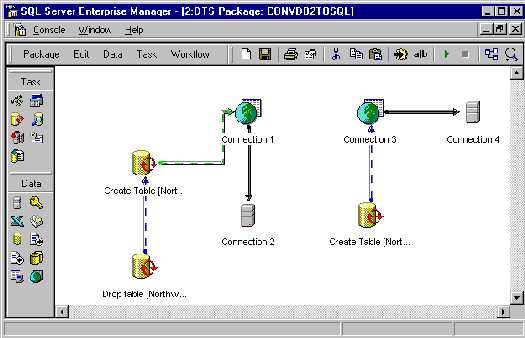
FIGURE 8

