There are two major options for securely exposing access to your MySQL database over an unsecured network: an SSL connection or an SSH tunnel. The CData MySQL Driver provides a secure, live data connection to MySQL data from popular BI & Analytics, data warehousing, and application development tools, supporting both SSL connections and SSH tunneling. In this article, we explore how to use the CData MySQL Driver with SSH tunneling, which is often easier to build and more secure than SSL due to the driver’s built-in support for tunneling.
In addition to supporting encryption through SSH security protocols, which provide a strong record against attacks, MySQL can be configured to only accept traffic from 'localhost,' blocking all connections except for the configured tunnel.
An SSH tunnel requires the SSH server to run in the same environment as the MySQL instance, but setting up a tunnel is simple once the server is up and running. SSH employs robust encryption and, via the tunnel, makes client connections appear to come from the SSH server, rather than from a remote client. You don't have to configure your MySQL server to allow remote connections when using an SSH tunnel so your MySQL instance is safe.
Configuring the SSH Client
Each CData MySQL connector has connection properties that allow you to connect to a MySQL instance through an SSH server. To connect, you will need to set Use SSH to "true" and set the following properties:
- SSH Client Cert: The name of the certificate store, path to the client certificate file, or the contents of the client certificate
- SSH Client Cert Subject: The subject used to search for the certificate in the specified store (default "*")
- SSH Client Cert Type: The type of key store containing the SSH client certificate
- SSH Client Cert Password: The password for the SSH client certificate (if required)
- SSH User: The username for the SSH server
- SSH Password: The password for the SSH user
- SSH Server: The location of the SSH server
- SSH Server Fingerprint: The fingerprint of the SSH server
- SSH Port: The port of the SSH server (default: 22)
An example of a configured SSH client in the CData ODBC Driver is shown below; the connection can be configured in any CData connector.
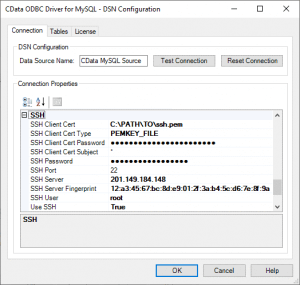
Depending on the connector, you may need to configure a connection string similar to the following:
User=myUser; Password=myPassword; Database=NorthWind; Server=myServer; Port=3306; UseSSH=TRUE; SSHClientCert="/home/ssh.pem"; SSHClientCertSubject=*; SSHClientCertType=PEMKEY_FILE; SSHClientCertPassword=""; SSHUser=root; SSHPassword=""; SSHServer=123.456.789.012; SSHServerFingerprint=""; SSHPort=1022
Because the SSH client is built directly into the connectors, the setup and usage is exactly the same, regardless of the operating system. Set the connection properties and start working with remote MySQL data from your local system, all through a secure SSH tunnel.
MySQL Connectivity Options
The built-in SSH client in the CData Connectors for MySQL allows you to simply connect to a MySQL instance through an SSH tunnel. CData provides standards-based MySQL connectors for ODBC, JDBC, ADO.NET, Python, and other technologies. In addition, CData offers drivers with the same built-in SSH tunneling capabilities to access every major database. You can get free 30-day evaluations of all drivers on the CData site.

