Try asking your colleague what is the difference between business intelligence
and a data warehouse. I find that a lot of people, even those who work in BI projects
and BI industry, do not understand the difference. A lot of people use these
2 terms interchangeably. Some people even prefer to use 1 term instead of the
other because it simply "sounds better". Many people think that business
intelligence is not just a data warehouse, but there is more to it. But when
asked "what business intelligence systems are not data warehouse systems?"
or "what part of business intelligence systems are not data warehouses?",
most of them have difficulties explaining the answer.
These days, "business intelligence" is the norm used by most vendors
in the industry, rather than "data warehouse". Most of them call /
classify their tools as business intelligence software, not data warehouse software.
The name of Cognos
product is "Cognos 8 Business Intelligence". BusinessObjects
label themselves as "BI software company" and "global leader
in BI software". The name of one of Hyperion
products is "Hyperion System 9 BI+". SAS
Enterprise BI Server provides a fully integrated and comprehensive suite
of business intelligence software. Microsoft
promotes SQL Server 2005 as the end-to-end business intelligence platform. It
seems that only Kimball Group who
consistently use the term data warehouse. Bill
Inmon, as the inventor of this term, also uses the term data warehouse.
So, let's get into the details. This is an example of a data warehouse system:
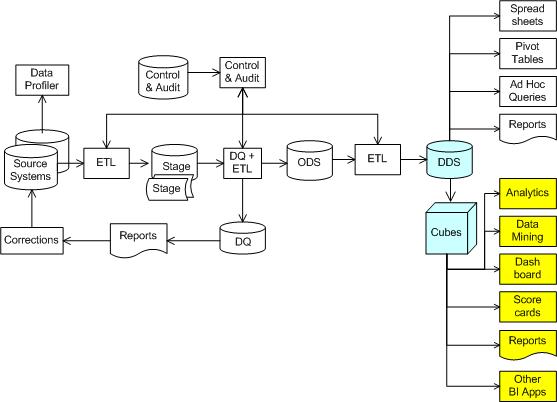
It includes ETL from the source system, front end applications (those 10 boxes
on the right hand side), and everything in between. It has a control system,
an audit system and a data quality system (also known as data firewall). Not
all data warehouse systems have all the components pictured above, for example,
some data warehouse system may not have operational data stored (ODS), see this
article for details.
The 2 blue items are data warehouse databases. The cylinder is in relational
format (labelled as dimensional data store, DDS for short), the box is in multidimensional
format (labelled as cubes in the picture above). This blue cube is also known
as on line analytical processing cube, or OLAP cube for short.
The yellow items are business intelligence applications. Most business intelligence
applications take data from multidimensional format data warehouse, but some
do take data from the relational format. The whole diagram above is also known
as business intelligence system.
Some business intelligence applications take data directly from the source
system. For example, some dashboard systems may get sales summary data from the source
system and display it in gauge meter format. In this case, we can not call the
system a data warehouse system. It is still a business intelligence system,
but it is not a data warehouse system, because it does not have a data warehouse
database behind the gauge meter application.
Business intelligence systems, in the past also known as executive information
systems, or decision support systems, are a non transactional IT system used to
support business decision making and solve management problems, normally used
by top executives and managers. Many
varied definitions exist in the market place today about the business intelligence
system; one
from Dr. Jay Liebowitz is arguably one of the better ones. Most people agree
that OLAP and data warehouse systems are a major and important part of business
intelligence systems. Most business intelligence systems are in the form of a
data warehouse systems. Yes, there are business intelligence systems that do
not use OLAP or data warehouses, as illustrated in the example of gauge meter
application above, but they are more rare than the ones with OLAP or a data warehouse.
According to Ralph Kimball, in his book The
Data Warehouse ETL Toolkit, a data warehouse is a system that extracts,
cleans, conforms, and delivers source data into a dimensional data store and
then supports and implements querying and analysis for the purpose of decision
making. He stressed that a data warehouse is not a product, a language,
a project, a data model or a copy of transaction system. In an interview
with Professional Association for SQL Server (PASS) on 30th April 2004,
he explained about the relationship between data warehousing and business intelligence.
In their latest book, The
Microsoft Data Warehouse Toolkit, Joy Mundy and Warren Thornthwaite do not
differentiate data warehouse systems and business intelligence systems. They consistently
use the term DW/BI system throughout the book. This is understandable because,
as I describe above, most business intelligence systems are in the form of a
data warehouse system.
Bill Inmon, who invented the term
data warehouse, defines data warehouse as a source of data that is subject oriented,
integrated, nonvolatile and time variant for the purpose of management's decision
processes. He pointed that the term data warehouse was never trademarked or
copyrighted. As a result, anyone can call anything a data warehouse. He recently
defined a new term, DW 2.0, and this one is trademarked so nobody can change
the definition. He explained the architecture in his
article in dmreview, along with the differences between the first generation
of data warehouses and DW 2.0 and its advantages.
So, as a summary, back to the original question, what is the difference between
data warehouse and business intelligence? Most business intelligence systems
are based on data warehouse systems (the one with dimensional model, fact tables,
dimension, etc), but some business intelligence systems are not data warehousing,
i.e. taking data directly from the source system, like the example described
above. Business intelligence application (as opposed to business intelligence
system) is the yellow boxes on the diagram above, i.e. the front end applications.
The data warehouse database (or sometimes people dropped the word database, so it
becomes just 'data warehouse') is the blue cylinder and blue box on the diagram
above, i.e. the dimensional storage, whether in relational database format or
in multidimensional database format.
If people say 'data warehouse', be careful because it can mean either data
warehouse system (the whole diagram above) or data warehouse database (just
the blue items). If people say 'business intelligence', it can mean either business
intelligence system (the whole diagram above, or a BI system without data warehouse)
or business intelligence application (the yellow boxes).
I hope this article makes the terms clearer, but I am open to comments and
suggestions. As Ralph Kimball said, if you ask 10 different people what data
warehouse is you are likely to get 10 different answers.
Vincent Rainardi
1st May 2006


