Applications
that provide services like data analysis, projections and any other data
services on client specific data are required to support, data import/upload
feature. Frequently clients of the application, upload data files to update the
application with client specific data. Supporting data import functionality is
common requirement for most of the financial applications. This is more the
case with web-based applications supporting many clients with ASP architecture.
Building robust functionality with maximum re-use of existing infrastructure and
investment with little or no development is the goal for many businesses. This
article is about using SQL Server DTS packages to achieve this goal. With
minimum development, all the functionality required for data imports can be
achieved with DTS programming in SQL Server.
Environment required for running the samples:
-
Windows NT/2000
-
SQL Server 2000
-
Microsoft Excel 97/2000
Assumptions:
-
Readers should be familiar with Databases and little bit of SQL/VB
script.
Author information:
- Please see the at the end
of article for more information on author
What is included in the
sample download file?
-
README.TXT file with instructions on installing sample
-
Trade Analysis sample database with key tables (SQL Script)
-
Sample import .xls file
-
Sample Import DTS package that can be used as starting point for all
import functionality. (DTS package is in structured storage file format and can
be opened by Enterprise manager)
SQL Server DTS
programming:
DTS (Data
Transformation Services) in SQL Server is very powerful feature and can be used
to solve many database related issues starting from data migration, conversion
and import/export. Even content publication/management applications can be
developed easily using DTS. SQL Server’s DTS support is extended with latest
version of SQL Server 2000. This article’s main goal is not only to expose the
DTS functionality of SQL Server but also to show the simplicity in using DTS
packages to implement core functionality.
General Business Requirement: Common
functionality required for Data imports:
-
Get client files through FTP
-
Schedule imports to run regularly (mostly every night)
-
Read client data files and validate data formats
-
Apply any business rules on data
-
Calculated any required columns, convert import data and massage data to
fit to application supported data format.
-
Import the final massaged data into application database conditionally:
-
Insert if data is not present (based on certain key information)
-
Update existing records, in case if data is present
-
Delete records based on some criteria (Not a frequent requirement though)
-
Clean up files that are imported once data import is done
-
Error/Log information on each row imported
-
Email/Notify administrators of any critical errors.
All above functionality can be achieved with SQL Server,
using DTS packages and SQL Agent (following list shows some key items that can
be used to achieve this):
-
DTS FTP Task
-
SQL Agent ( for scheduling any DTS package)
-
Text drivers to read data files (Ex: Excel or .csv)
-
DTS Data Transfer task with ActiveX Script tasks
-
Business validation/conversion logic can be implemented in COM objects,
which can be called from ActiveX script tasks.
-
Conditional Data Pump constants returned by ActiveX script to handle
Insert/Update/Delete
-
Error/Log support through database log table
-
Email notification using DTS Email task
Case study:
This case
study takes up a sample financial web application “Trade Analysis” designed and
developed by Prakash Financials. Trade Analysis application supports trade
analysis for client specific trade data. Client in this article represents
mostly an organization. ‘User’ is any user that uses the services of “Trade
Analysis”. There may be many users from one single organization/client and there
may be more than one client registered for the using “Trade Analysis”. When an
organization decides to use “Trade Analysis”, few users from the organization
are registered with “Prakash Financials”, with same or different access
privileges.
Note: There is no
organization really exists like ‘Prakash Financials’. Any and all names are used
in this document as an example and do not refer any real entity.
Trade data for analysis:
“Trade
analysis” provides analysis on trade data. But trade data is specific to each
client. Also for each client Trade data changes daily depending on the client
business. Clients use their own trade applications to post trades. So this data
has to be uploaded to “Trade Analysis” application so that client can see the
reports/analysis on their latest data. Mostly client reporting or data analysis
requirements do not need to be online or in sync with Trade postings. After
trades are posted, client is interested is seeing results from “Trade Analysis”
at the end of the day.
Need for automation:
“Trade
analysis” product currently supports similar functionality through manual feeds,
with business users in “Prakash Financials” manually entering data for different
clients. With few clients accessing the system it was acceptable before. But now
the number of clients using the application is growing and few clients have
requirements to see the changes as quickly as possible. Also there is no
consistent way of importing data with manual data-entry as it depends on the
skill levels of business uses. All this is pushing “Prakash Financials” to
automate the process of client data import.
Goal for data import:
-
Solution needs to be implemented in aggressive schedule
-
There is no room for error
-
It should be very cost effective and easy to maintain
-
Should support all the functionality for data import specified in “Common
functionality required for Data imports” section above.
Design approach:
Prakash
Financials Design team evaluated existing infrastructure and did a gap analysis.
Current application uses SQL Server for all its data requirements. Considering
this it seemed appropriate to use SQL Server DTS package and SQL Agent to
support data import functionality. Seeing that this approach can achieve all the
above goals for business, project is approved for development.
“Trade Analysis”
database:
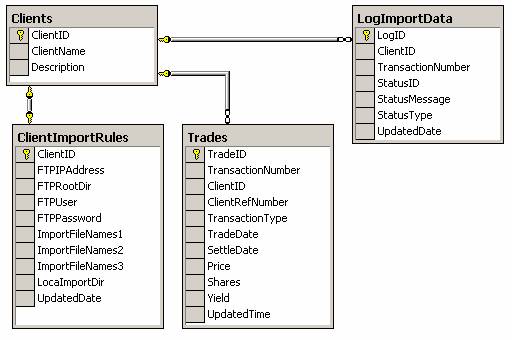
Trade analysis
database has a main table “Trades” which will be used in data import and other
details are ignored in this article for simplicity. There is also a new table
added for the purpose of error/status logging. Following are details of main
tables in “Trade Analysis” database:
Fig.1 : “Trade Analysis” application
database with key tables.
Client import data
format:
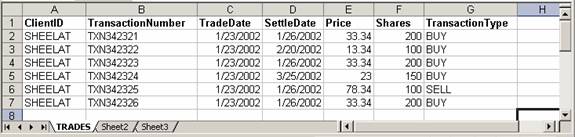
Clients are
expected to provide “Trade” files from client systems in a specific format that
is acceptable by “Prakash Financials”. .CSV/Text format files and Excel files
are very widely used data files in the industry for data import/export. Many
clients of Prakash Financials have applications that import/export data to excel
files. So it is agreed to support excel files with trade data in excel tab with
name “TRADES”. There may be more tabs in excel file imported from client but
they may not be used currently in data import.
Fig. 2: Sample Client trade import file
format
Client FTP
Configuration:
Clients will configure FTP sites and give
access information to Prakash Financials so that client data files can be
imported through FTP.
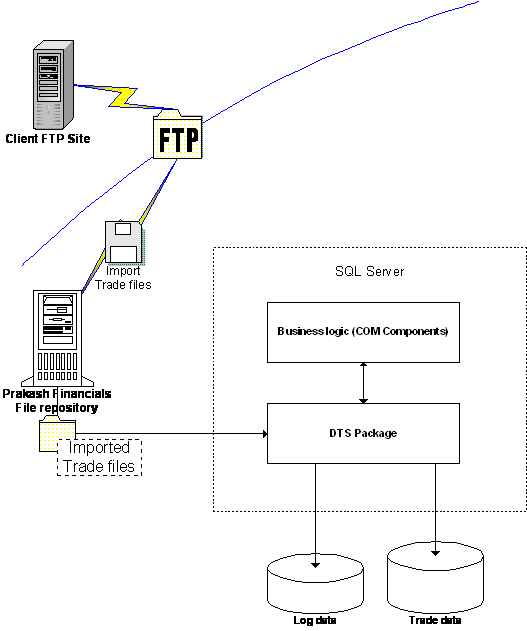
Fig. 3
Data import functionality details
Implementing Data Import
functionality:
Fig.3 shows
high level details of data import functionality. There are existing COM
components that are used in business logic block to calculate some trade data
elements (ex. Yield). Following are the details of building DTS package:
Assumptions:
Following
section assumes that SQL Server 2000 is used for implementing DTS packages and
user creating DTS package has required access/admin privileges to do that.
Creating DTS Package:
Step 1: Create new directory to store the
imported trade files locally. (Ex: C:\TA_Imports directory)
Step 2: Create new DTS Package (‘TA_DBImport’)
-
Open SQL Server Enterprise manager
-
Open the SQL Server where Trade Analysis database resides (Register the
SQL Server is not already present in the enterprise manager)
-
Under “Data Transformation Services” -> Local packages” -> Right
click->Select “New package”.
Step 2: Create FTP Task
-
Drag and drop “File Transfer Protocol task” from left side icon list,
below “Task” heading.
-
When prompted with FTP Properties, ignore
NOTE: We will see how to change
these attributes dynamically later.
Step 3: Create Dynamic Properties Task
-
Drag and drop “Dynamic Properties task” from left side icon list, below
“Task” heading.
-
When prompted with popup window, click ‘Add’ button
-
In the new window opened, Expand ‘Task’ node in the left side tree.
-
Select item that says ‘DTSTask_DTSDynamicProperties_Task…
-
Select the property item on right side that says something like
‘Description’
-
Click ‘Set’ button at the bottom of the window.
-
Now in the popup: Select ‘Global Variables’ option in ‘Source’ combo box
-
Click on ‘Create Global Variables’ button
-
Add following variables (all string datatype)
1.
FTPIPAddress
2.
FTPRootDir
3.
FTPUser
4.
FTPPassword
5.
ImportFileNames
6.
LocalImportDir
-
Now click ->OK ->Cancel->Close->OK buttons, so that you will be in the
package main window. (Careful, don’t close the package yet)
Step 4: Create a temporary trade import excel
file (Ex: Trades.xls) under C:\TA_Import directory
-
Enter column headings for all the required columns for import, in the
first line
-
You can enter some test data in the second line
-
Name the tab where this information is entered as “TRADES”.
Please see section “Client Data
Import format” above for more details.
Step 5: Create connection object “Excel
97-2000”
-
Drag and drop “Microsoft Excel 97-2000” connection icon from left side
icon list, below “Connection” heading.
-
In the popup window for “File Name” prompt enter “C:\TA_Import\Trades.xls”
(created in step 4).
Step 6: Create connection object - “OLEDB
Provider for SQL Server”
-
Drag and drop “Microsoft OLEDB Provider for SQL Server” connection icon
from left side icon list, below “Connection” heading.
-
In the popup window enter following details
-
Select database server where “Trade Analysis” database resides
-
Select proper authentication scheme
-
Select “Trade Analysis” database from the list
Step 7: Create “Data Driven Query Task”
(This is the import task that implements a lot of functionality)
-
Drag and drop “Data Driven Query Task” icon from left side icon list
below ‘Task’ heading.
-
In the Source Tab:
-
Connection: Select “Microsoft Excel 97-200” connection
-
Table/View: Select “TRADES$” from the combo box. (Try Preview to see test
data)
-
In Bindings Tab:
-
Connection: Select “Microsoft OLEDB provider for SQL Server” connection
-
Table name combo box: Select “Trades” table
-
In Transformations Tab:
-
Name: Select “DTSTransformation__1” item
-
(This should show Type grayed as ‘ActiveX task’)
-
Click ‘Edit’ button on this
-
Now you see window with Transformation Options. Do the following
-
Select ‘SourceColumns’ tab - click button “<<” first and click “>>”
button
-
Select ‘Binding Columns’ tab- click button “<<” first and click “>>”
button
-
Select ‘General Tab’ and click ‘Properties’ – you will now see the
ActiveX script where you can decide the fate of each row imported.
Select OK->OK->OK and come back
to the main package window.
NOTE: It is easier to see
the details from DTS sample supplied with this article. Also please see SQL
Server documentation for better understanding of this task.
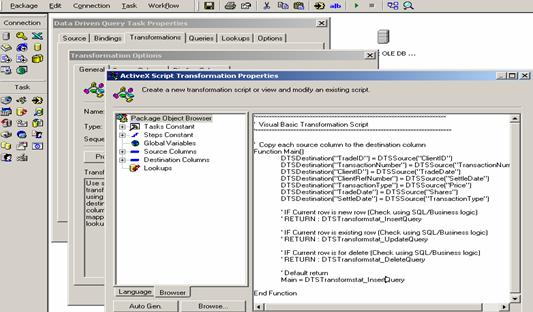
Fig. 4. ActiveX
script window with sample Code for transformation
Step 8: Create Queries for
Insert/Update/Delete in “Data Driven Query Task”/ Queries tab
-
Double click the “Data Driven Query Task” created in Step 6.
-
You will need to enter queries for Insert/Update/Delete with ‘?” as
placeholders where you expect values to be filled up by ActiveX script in Step
6.
Fig. 5: Sample Query entry
for Insert Query type
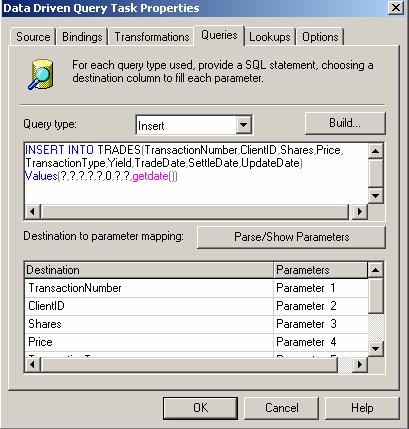
NOTE: It is easier to see
the details from DTS sample supplied with document for this. Also please see SQL
Server documentation for better understanding of this task.
Step 9: Create “Send Mail Task”
-
Drag and drop “Send Mail Task” icon from left side icon list below ‘Task’
heading.
-
Configure mail task with status details and list of support email ids.
(Machine should be configured correctly so that mail is delivered to target
users).
Fig. 6: DTS Package : Designer diagram
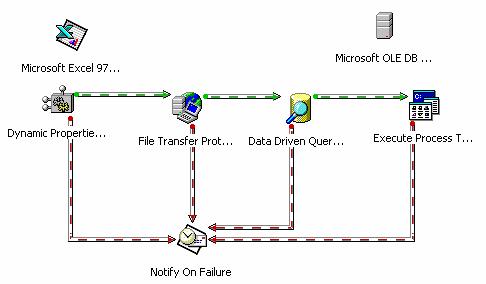
Above diagrams shows the main
tasks linked using DTS Designer (SQL Server Enterprise manager). Green lines
represent (On Success) and Red Lines for “On Failure” paths.
As you see from Fig.6, Dynamic
Properties task is executed first so that it will read FTP properties and Local
import directory settings from “ClientImportRules” table. FTP Task and Excel
Connection Object are configured in “Dynamic Properties task” to have correct
values at runtime. See the sample DTS package supplied with this article for
more details on this.
TIP: Reading more than
one file with FTP task: ClientImportRules.ImportFileName1 column can have more
than one file specified using the format ‘<Name of the file>’;’<Ftp dir path –
excl. root path>’;’’;…. If FileName1 column is not enough to enter all details
you can continue it in FileName2, FileName3 columns of ClientImportRules table.
In this case change necessary logic in “Dynamic Properties Task” to read
“FTPImportFileNames” variable.
FTP File name
format: ‘<FileName>’ ; ‘<Path>’ ; ’<size>’
; ‘<FileName>’ ; ’<path>’ ; ’<size>’
Size can be
empty ‘’, but need to be specified in the string.
Configuring each task:
There are few
tasks that are required to configure FTP task and ‘Excel Connection’ object.
Error handling and logging also need to be incorporated in “Data Driven Query”
and “Send Mail” tasks. Following are high level details of how this is done.
Attached DTS file should give more details.
-
Open ‘Dynamic Properties’ and read all Global variables from Query type
using ‘ClientImportRules’ table.
Workflow implementation:
All the tasks created above,
should be linked properly so that only on success next task is called. It is
very easy to create workflow and linking tasks conditionally.
-
Press “Shift key” - select “Source Task” and “Target Task” > Select
“Workflow” menu and select appropriate connection (On Success, On Complete, On
Failure).
Saving DTS Pakage:
Now we are done with creating DTS Package.
Select ‘Package->Save’ menu option. Select ‘SQL Server’ as default in ‘Location’
and give some package name. (Please see SQL Server documentation for other types
of storate).
Debugging and testing
DTS package
To debug and test DTS package do the following:
-
Verfiy the data in all the tables and make sure that ClientImportRules
table has correct information.
-
Check FTP site to see if it is running and userid/password has access to
specific resources
-
Executing Entire package: Right click on the package in SQL Enterprise
Manager and select “Execute Package”. You will see the result window showing
exact tasks that are executed with the status iformation.
TIP: It is not recommended
that you execute the whole package at once, if you are testing it for the first
time. Best approach is to test individual tasks and execute each tasks manually,
to see if each tasks works the way it is inteneded.
-
To execute each individual task in the package separately: Open the
Package in SQL Enterprise manager, right click on each task and select “Execute
task” menu option.
Scheduling DTS Package:
-
Select “Data Transformation Services”->Local Packages-> and select “DTS
Package” created above.
-
Right click on the package and select “Schedule package” option and
select the scheduling options.
NOTE: For scheduler to work
correctly you need to have “SQL Agent” service running. To check this :
- Login to the machine where SQL
Server is running
-
Open Start->Program Files->Administrative Tools->Services (open Services
window)
-
Make sure that service named “SQL Agent” has status “Started” and
settings as “Automatic” start option.
Calling businesscomponents to calculate data elements or manipulate data:
Before
inserting imported data many applications might require calculating some values
or manipulating data, using few business components. Also depending on the data
elements, imported data needs to be either inserted as new row or update
existing row. This logic can be implemented in the “ActiveX script window” in
“Transformation” tab of “Data Driven Query Task”. Please see Step: 7 for mote
info.
ActiveX Script
method “Main” (In ActiveX script of “Data Driven Query task”) is called each
time a new row is imported. Depending on what value the “Main” method returns,
data is either inserted or updated. For each return type there should be
respective Query type defined with actual database query in “Query” tab of “Data
Driven Query Task”.
Sample Code listing:
Example ActiveX script is presented below:
'**********************************************************************
' Visual Basic Transformation Script
'************************************************************************
' Copy each source column to the destination column
Function Main()
‘COMMENT: Map source columns to
Destinationcolums here.
‘All destination columns can be used as
parameters in queries entered in ‘Query’ tab later.
DTSDestination("ClientID") =
DTSSource("ClientID")
DTSDestination("TransactionNumber") =
DTSSource("TransactionNumber")
DTSDestination("TradeDate") =
DTSSource("TradeDate")
DTSDestination("SettleDate ") =
DTSSource("SettleDate")
DTSDestination("Price ") = DTSSource("Price")
DTSDestination("Shares ") =
DTSSource("Shares")
DTSDestination("TransactionType ") =
DTSSource("TransactionType")
‘ COMMENT: Call any business components
here. Following is only a sample.
Dim oBusObj
Set oBusObj = CreateObject(“PKBus.CalcEng”)
DTSDestination(“Yield”) = oBusObj.CalcYield
' COMMENT:IF Current row is new row (Check
using SQL/Business logic)
' RETURN : DTSTransformstat_InsertQuery
' COMMENT: IF Current row is existing row
(Check using SQL/Business logic)
' RETURN : DTSTransformstat_UpdateQuery
' COMMENT: IF Current row is for delete
(Check using SQL/Business logic)
' RETURN : DTSTransformstat_DeleteQuery
' COMMENT:Default return
Main = DTSTransformstat_InsertQuery
End Function
Logging status
information for each row:
As you see from
above ActiveX script that, for every row “Main” method is called and return type
of the script decides which query to run from pre-defined set of queries. So it
is possible to handle logging as a part of queries in “Queries” tab or through
script.
TIP:
You can create stored procedure in and call the stored procedure in “Queries”
tab with different parameters, instead of using SQL directly.
Conclusion:
Article tries
to cover key features of DTS without losing focus on minute details. Sample code
is supplied for this purpose, so that more implementation details can be
presented. Please use the sample code to learn more about DTS. Code supplied is
not of production quality and it is written only to show how to use specific
feature/functionality.

