DBA Tools: sp_whocpu
In recent years I often needed to quickly identify the processes that consume the most CPU on the server in real time, without settin up traces.
If you try to run sp_who2 and base your investigation on the CPUTime listed there, you will find that the processes showing the highest figures, might not be in fact those that consume the most CPU in real time.
This is because sp_who2 displays the total CPUTime accumulated since the connection was established, therefore sp_who2 can show high CPUTime ficures, which do not reflect the current activity on the server.
In order to get an indication on the real time CPU for the user processes, I have modified the sp_who2 stored procedure to include a new metric.
The result is called sp_whocpu and in addition to the usual columns returned by sp_who2 it contains a new metric that I introduced, called CPU_Delta.
The CPU_Delta is calculated by sampling the CPU readings over a period of time, and returns accurate figures in milliseconds about the CPU activity per process. I found that setting the sampling period at 3 seconds is a good choice for calculating the CPU_Delta.
Like in any sampling process, increasing the sampling period and the number of samples taken would increase the accuracy. However, three seconds is a period that I found suited for this, as it is also the time you have to wait before getting any output from sp_whocpu.
The stored procedure sp_whocpu orders the output by CPU_Delta in descending order, therefore making it easy to rapidly identify the top CPU consumers on the server.
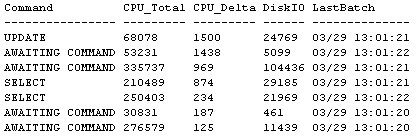
The CPU_Total time is the same figure as the one returned by sp_who2 which appears listed there as just CPUTime. The CPU_Delta figure is the CPU time consumed within the 3 seconds sampling period.

From the figure above you can immediately see that the process having the highest CPU at the time of the investigation, is not the process that has the highest accumulated cpu (CPU_Total). It would be therefore impossible to determine the highest momentary CPU only based on what the standard sp_who2 returns.
I hope that sp_whocpu is going to prove as useful to you as it is for me in investigating performance issues.
use master
go
if exists (select * from master.dbo.sysobjects where id = object_id('dbo.sp_whocpu') )
Drop Procedure dbo.sp_whocpu
go
/*====================================================================
-- Mircea Anton Nita - 2010
-- https://www.mcpvirtualbusinesscard.com/VBCServer/Mircea/card
======================================================================*/Create Procedure dbo.sp_whocpu
@dbname sysname = null,
@loginame sysname = null
as
set nocount on
declare
@retcode int
,@sidlow varbinary(85)
,@sidhigh varbinary(85)
,@sid1 varbinary(85)
,@spidlow int
,@spidhigh int
,@seldbid varchar(10)
,@charMaxLenLoginName varchar(24)
,@charMaxLenDBName varchar(24)
,@charMaxLenCPUTime varchar(10)
,@charMaxLenCPUDelta varchar(10)
,@charMaxLenDiskIO varchar(10)
,@charMaxLenHostName varchar(24)
,@charMaxLenProgramName varchar(10)
,@charMaxLenLastBatch varchar(10)
,@charMaxLenCommand varchar(10)
,@charsidlow varchar(85)
,@charsidhigh varchar(85)
,@charspidlow varchar(11)
,@charspidhigh varchar(11)
,@command varchar(8000)
-- set defaults
set @retcode = 0
set @sidlow = convert(varbinary(85), (replicate(char(0), 85)))
set @sidhigh = convert(varbinary(85), (replicate(char(1), 85)))
set @spidlow = 0
set @spidhigh = 32767
if (@dbname is not null)
set @seldbid = cast((select top 1 dbid from master.dbo.sysdatabases where name like '%'+@dbname+'%') as varchar(10))
else
set @seldbid = '0'
if (@loginame is null) -- Simple default to all LoginNames.
GOTO LABEL_PARAM
select @sid1 = null
if exists(select * from sys.syslogins where loginname = @loginame)
select @sid1 = sid from sys.syslogins where loginname = @loginame
if (@sid1 is not null) -- The parameter is a recognized login name.
begin
select @sidlow = suser_sid(@loginame)
,@sidhigh = suser_sid(@loginame)
GOTO LABEL_PARAM
end
if (lower(@loginame collate Latin1_General_CI_AS) in ('Active')) -- Special action, not sleeping.
begin
select @loginame = lower(@loginame collate Latin1_General_CI_AS)
GOTO LABEL_PARAM
end
if (patindex ('%[^0-9]%' , isnull(@loginame,'z')) = 0) -- Is a number.
begin
select
@spidlow = convert(int, @loginame)
,@spidhigh = convert(int, @loginame)
GOTO LABEL_PARAM
end
raiserror(15007,-1,-1,@loginame)
select @retcode = 1
GOTO LABEL_RETURN
LABEL_PARAM:
-- Getting data over a time window to allow the cpu_delta metric calculation
if object_id('tempdb.dbo.#cpu1') is not null drop table #cpu1
if object_id('tempdb.dbo.#cpu2') is not null drop table #cpu2
select spid, cpu into #cpu1 from master.dbo.sysprocesses with (nolock) order by cpu desc
waitfor delay '00:00:03'
select spid, cpu into #cpu2 from master.dbo.sysprocesses with (nolock) order by cpu desc
-------------------- Capture consistent sysprocesses. -------------------
select
sp.spid
,status
,sid
,hostname
,program_name
,cmd
,sp.cpu
,c2.cpu-c1.cpu as 'cpu_delta'
,physical_io
,blocked
,dbid
,convert(sysname, rtrim(loginame)) as loginname
,sp.spid as 'spid_sort'
, substring( convert(varchar,last_batch,111) ,6 ,5 ) + ' '
+ substring( convert(varchar,last_batch,113) ,13 ,8 ) as 'last_batch_char'
into #tb1_sysprocesses
from #cpu2 c2 join #cpu1 c1 on c2.spid = c1.spid join master.dbo.sysprocesses sp with (nolock) on sp.spid = c2.spid
where c2.cpu-c1.cpu > 0
if @@error <> 0
begin
select @retcode = @@error
GOTO LABEL_RETURN
end
if (@loginame in ('active'))
delete #tb1_sysprocesses
where lower(status) = 'sleeping'
and upper(cmd) in (
'AWAITING COMMAND'
,'LAZY WRITER'
,'CHECKPOINT SLEEP'
)
and blocked = 0
and dbid <> @seldbid
-- Prepare to dynamically optimize column widths.
select
@charsidlow = convert(varchar(85),@sidlow)
,@charsidhigh = convert(varchar(85),@sidhigh)
,@charspidlow = convert(varchar,@spidlow)
,@charspidhigh = convert(varchar,@spidhigh)
select
@charMaxLenLoginName =
convert( varchar
,isnull( max( datalength(loginname)) ,16)
)
,@charMaxLenDBName =
convert( varchar
,isnull( max( datalength( rtrim(convert(varchar(128),db_name(dbid))))) ,20)
)
,@charMaxLenCPUTime =
convert( varchar
,isnull( max( datalength( rtrim(convert(varchar(128),cpu)))) ,10)
)
,@charMaxLenCPUDelta =
convert( varchar
,isnull( max( datalength( rtrim(convert(varchar(128),cpu_delta)))) ,10)
)
,@charMaxLenDiskIO =
convert( varchar
,isnull( max( datalength( rtrim(convert(varchar(128),physical_io)))) ,6)
)
,@charMaxLenCommand =
convert( varchar
,isnull( max( datalength( rtrim(convert(varchar(128),cmd)))) ,7)
)
,@charMaxLenHostName =
convert( varchar
,isnull( max( datalength( rtrim(convert(varchar(128),hostname)))) ,16)
)
,@charMaxLenProgramName =
convert( varchar
,isnull( max( datalength( rtrim(convert(varchar(128),program_name)))) ,11)
)
,@charMaxLenLastBatch =
convert( varchar
,isnull( max( datalength( rtrim(convert(varchar(128),last_batch_char)))) ,9)
)
from
#tb1_sysprocesses
where
spid >= @spidlow
and spid <= @spidhigh
-- Output the report.
set @command = '
set nocount off
select
SPID = convert(char(5),spid)
,Status =
CASE lower(status)
When ''sleeping'' Then lower(status)
Else upper(status)
END
,Login = substring(loginname,1,' + @charMaxLenLoginName + ')
,HostName =
CASE hostname
When Null Then '' .''
When '' '' Then '' .''
Else substring(hostname,1,' + @charMaxLenHostName + ')
END
,BlkBy =
CASE isnull(convert(char(5),blocked),''0'')
When ''0'' Then '' .''
Else isnull(convert(char(5),blocked),''0'')
END
,DBName = substring(case when dbid = 0 then null when dbid <> 0 then db_name(dbid) end,1,' + @charMaxLenDBName + ')
,Command = substring(cmd,1,' + @charMaxLenCommand + ')
,CPU_Total = substring(convert(varchar,cpu),1,' + @charMaxLenCPUTime + ')
,CPU_Delta = substring(convert(varchar,cpu_delta),1,' + @charMaxLenCPUDelta + ')
,DiskIO = substring(convert(varchar,physical_io),1,' + @charMaxLenDiskIO + ')
,LastBatch = substring(last_batch_char,1,' + @charMaxLenLastBatch + ')
,ProgramName = substring(program_name,1,' + @charMaxLenProgramName + ')
,SPID = convert(char(5),spid) -- Handy extra for right-scrolling users.
from
#tb1_sysprocesses
where spid > 50 -- filter out system spids
and spid <> @@spid -- and current process spid
and spid >= ' + @charspidlow + '
and spid <= ' + @charspidhigh + '
'
if @seldbid > 0
set @command = @command +
'
and dbid = ' + @seldbid + '
'
set @command = @command +
' order by cast(cpu_delta as int) desc, cast(cpu as int) desc
set nocount on
'
exec (@command)
LABEL_RETURN:
if object_id('tempdb.dbo.#tb1_sysprocesses') is not null drop table #tb1_sysprocesses
if object_id('tempdb.dbo.#cpu1') is not null drop table #cpu1
if object_id('tempdb.dbo.#cpu2') is not null drop table #cpu2
return @retcode -- sp_whocpu
go
if exists (select * from sysobjects
where id = object_id('dbo.sp_whocpu')
and sysstat & 0xf = 4)
grant exec on dbo.sp_whocpu to public
go