A database administrator has various tasks and responsibilities. Managing and keeping track of the database is one of them. Whether you are new or an experienced database administrator, you must know how to get the list of tables because of following reasons
- It helps to understand the table structure and content of table.
- If you are familiar with the table structure, you can create desired and required indexes on it.
In SQL Server, we can get the list of tables by using any of the following methods:
- Querying information_schema.tables.
- Querying system catalog view like sys.tables and sys.objects.
- SQL Server management studio
Using these methods, this article contains example SQL queries to view the following information that can be useful to get the more details of table.
- View the list of temporal tables and associated history tables
- View the list of history table of temporal tables with their size.
- View the list of tables with constraints
- View the list of tables with indexes
- View list of tables with statistics update date
For demonstration, I am using the WideWorldImporters database.
Method 1: Querying information_schema.tables
Using information_schema.tables, you can query information about the tables in a database to help you understand the schema and structure of the database. We can use information_schema.tables view to populate the list of all tables created in the WideWorldImporters database. The information_schema.tables is a system view in SQL databases that provides metadata about tables in a database.
For example, you can use it to retrieve a list of all tables in a database or check whether a table exists. To retrieve the list of tables created in the WideWorldImporters database, run the SQL query specified below on SQL Server management studio or dbForge studio for SQL Server
USE WideWorldImporters GO SELECT t.TABLE_SCHEMA, t.TABLE_NAME, t.TABLE_TYPE FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES
Output

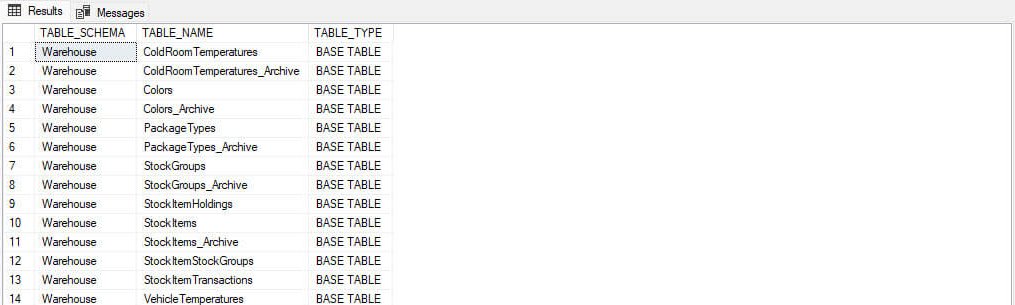
Suppose you want to filter the list of tables and populate only those tables created in Warehouse schema. In that case, you must apply filter on Table_schema column. The query can be written as following:
USE WideWorldImporters GO SELECT t.TABLE_SCHEMA, t.TABLE_NAME, t.TABLE_TYPE FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES t WHERE T.TABLE_SCHEMA='Warehouse'
Output
Method 2: Querying system catalog view and tables
The next method is populating the tables by querying system catalog views. The system catalog view in Microsoft SQL Server that provides metadata of tables in a database like table's schema, name, type, creation time, and other properties.
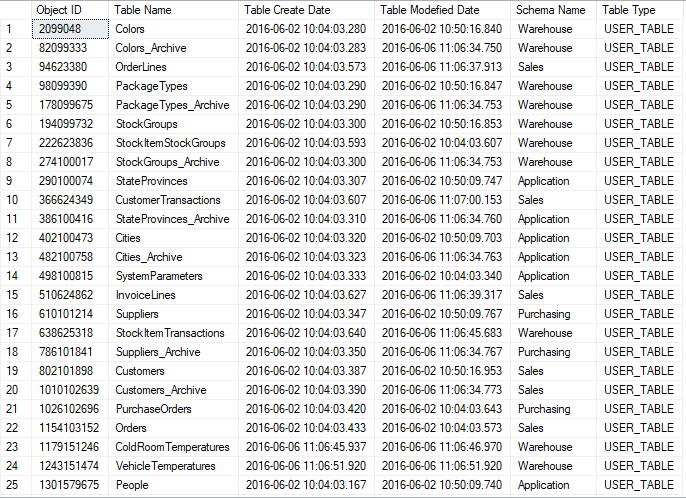
The following query gives you the list of tables created in wideworldimportors database with their object_id, type, create date, modified date and schema in which the table is created.
USE WideWorldImporters go SELECT object_id [Object ID], st.name [Table Name], create_date [Table Create Date] , modify_date [Table Modefied Date], ss.name [Schema Name] , type_desc [Table Type] FROM sys.tables st left join sys.schemas ss on st.schema_id =ss.schema_id
Output
Now, let us see some other example queries which can help to get more details of table.
Example 1: View the list temporal tables and associated history tables
Suppose, we are using system versioned temporal tables in our application. Temporal tables is a in-built feature which can be used to view the data, stored at specific point of time. You can read this article to learn more about system version temporal table. Now, we want to view the list of temporal tables and history table. You can To do that, we must apply filter on temporal_type column of sys.tables view. The query is written as following:
USE WideWorldImporters go SELECT t.name [Table Name], h.name [History Name], t.temporal_type_desc [Temporal Table Type], t.create_date [Create Date], T.history_retention_period [History retention], T.history_retention_period_unit_desc [History retention unit] FROM sys.tables t INNER JOIN sys.tables h ON t.history_table_id = h.object_id WHERE t.temporal_type = 2
Output

Note that the sys.tables have a column name object_id that can be used to join other system catalog views and populate the other details of the table.
Example 2: View the list of history tables of temporal tables with size
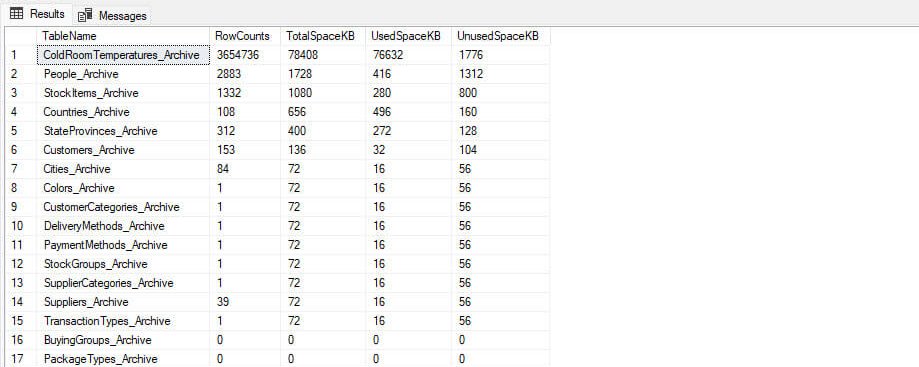
Sometimes we might want to check the list of temporal history tables with their size. To view the history table, we must apply filter on temporal_type column. To get the size of tables, we will join the sys.tables and sys.allocation_units catalog views and to get the record count of table, we are joining sys.tables with sys.partitions catalog views.
The query is following:
SELECT DISTINCT
t.name AS TableName,
SUM(p.rows) AS RowCounts,
SUM(a.total_pages) * 8 AS TotalSpaceKB,
SUM(a.used_pages) * 8 AS UsedSpaceKB,
(SUM(a.total_pages) - SUM(a.used_pages)) * 8 AS UnusedSpaceKB
FROM
sys.tables t INNER JOIN sys.indexes i ON t.OBJECT_ID = i.object_id
INNER JOIN sys.partitions p ON i.object_id = p.OBJECT_ID AND i.index_id = p.index_id INNER JOIN
sys.allocation_units a ON p.partition_id = a.container_id
WHERE t.temporal_type=1
GROUP BY
t.name, i.object_id, i.index_id, i.name ORDER BY TotalSpaceKB DESC
Output
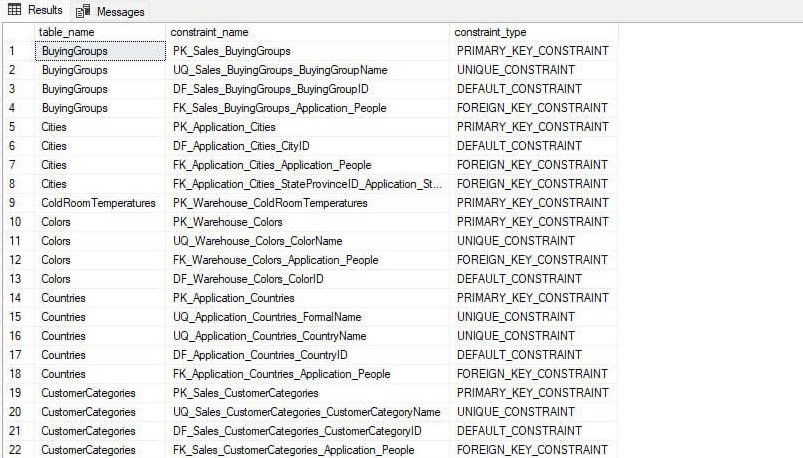
Example 3: Populate the list of tables with constraints
If we want to retrieve information about tables and their associated constraints in SQL Server. You can execute following T-SQL query.
Query
SELECT
t.name AS table_name,
c.name AS constraint_name,
c.type_desc AS constraint_type
FROM
sys.tables t INNER JOIN sys.objects c ON t.object_id = c.parent_object_id WHERE
t.type_desc = 'USER_TABLE' AND c.type_desc LIKE '%CONSTRAINT' ORDER BY t.name;
The above query joins sys.tables and sys.objects system views to retrieve the list of table and associated constraint.
Output
Now, let us see how to get the list of history tables of temporal table.
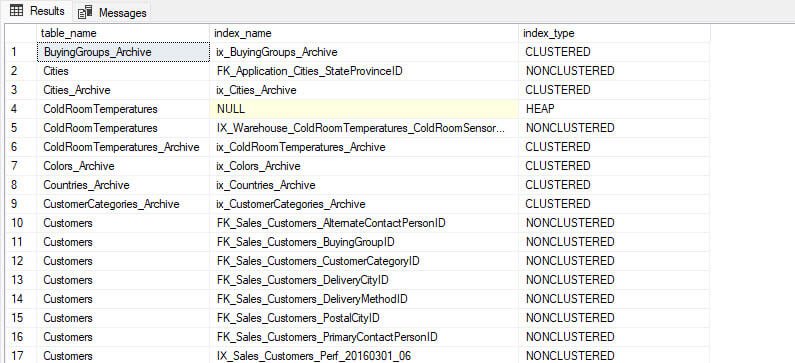
Example 4: Populate the list of tables with indexes.
This example shows how to get the list of tables that has indexes. To get the list we are joining sys.tables and sys.indexes catalog views.
Query
SELECT
t.name AS table_name,
i.name AS index_name,
i.type_desc AS index_type
FROM sys.indexes i INNER JOIN
sys.tables t ON i.object_id = t.object_id
WHERE i.is_primary_key = 0 AND i.is_unique_constraint = 0 AND i.is_unique = 0
ORDER BY t.name, i.name;
Output
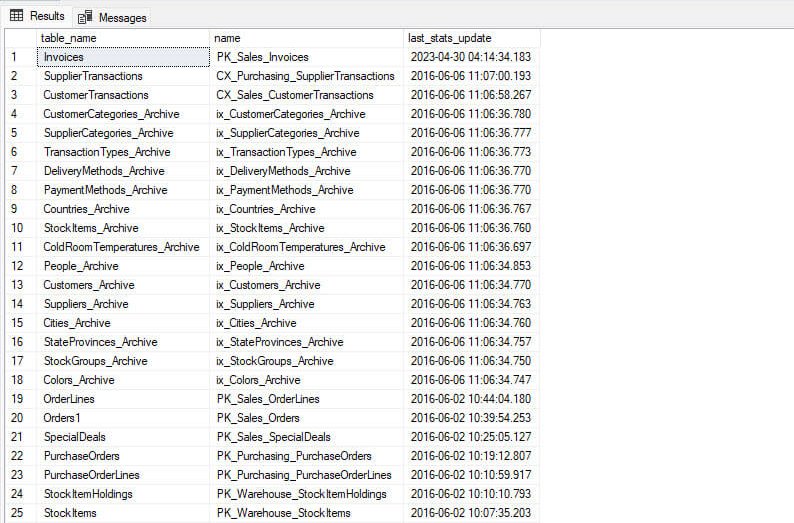
Example 5: Populate list of tables with statistics update date
In this example, we will see how to get the list of tables with their statistics update date. We can use STATS_DATE function to get the statistics update date of a table. You can read this article to learn more about STATS_DATE function. To find statistics update date of any index or tables, we must pass object id of a table and index_id of the table. We can get them by joining sys.tables and sys.indexes.
Below query gives you the details of tables with statistics update date.
SELECT
t.name AS table_name,
STATS_DATE(t.object_id, i.index_id) AS last_stats_update
FROM
sys.tables t
INNER JOIN
sys.indexes i ON t.object_id = i.object_id
WHERE
i.index_id <= 1
ORDER BY
last_stats_update DESC, t.name;
Output
Now, let us explore the third method to view the tables created in a database.
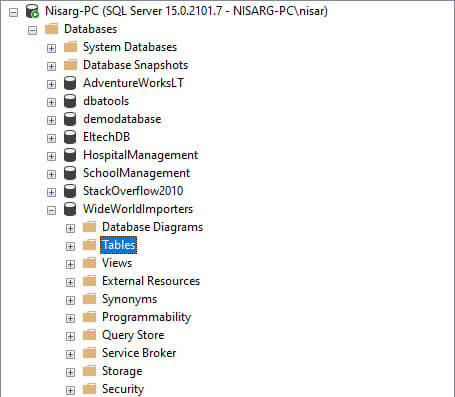
Method 3: View tables in SQL Server management studio.
We can view the list of tables from the object explorer of SSMS. Open SSMS --> Connect to database instance --> Expand Wideworldimportors database folder --> Expand tables. Here you can see the tables created in the WideWorldImporters database.
You can filter the list of tables by applying the appropriate filters on the table name. Right-click on the Table folder and select Filter Setting.
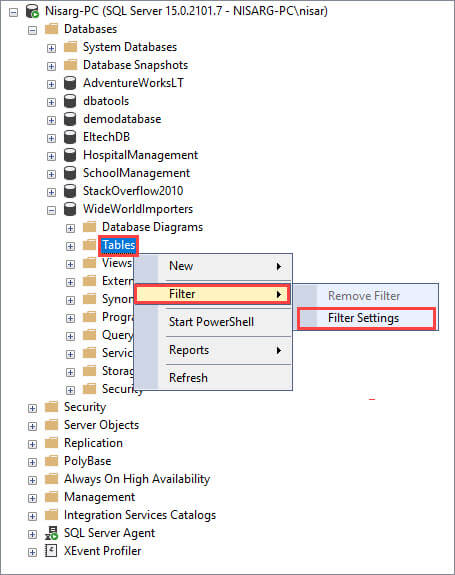
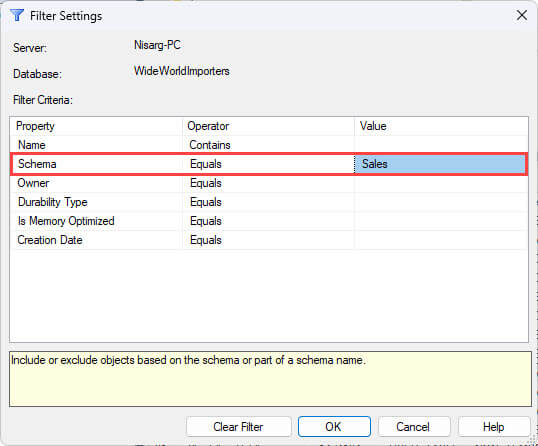
In the Filter Settings dialog box, you can apply filters on various properties of tables like name, schema, owner creation date, etc. You can filter tables by using Contains, Does not contain, and Equal operators. Suppose you want to find the tables of Sales schema, then the search parameters can be configured as follows:
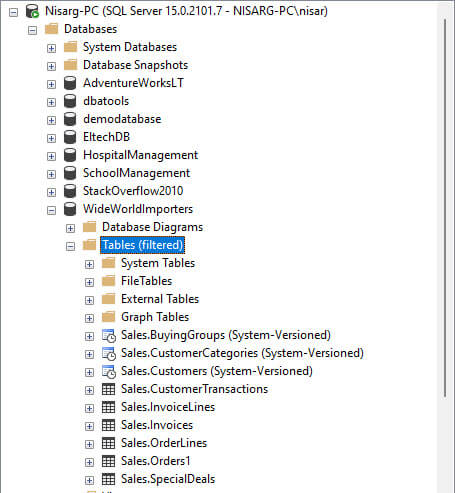
After applying the filter, the object explorer shows the list of tables in the Sales schema.
Summary
This article teaches us different methods to populate the list of tables created in a database. We learned how to get the table list using SQL Server management studio and system catalog views. Moreover, I have shown a few examples of populating table names with other properties of tables, like their size, the indexes created on them, etc. In the next article, I will show how we can use SQL Server reporting services to view the tables.