This post demonstrates the methods of PIT recovery of the database. The step by step details of the recovery process is explained below
The requirement for PIT restore/recovery is to setup a single node replica so that the oplogs can be used to “replay transactions” for point in time recovery. Oplog is a capped collection which stores all the transactions in an order. Oplog can be queried like other collections.
https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/core/replica-set-oplog/
Have used two instances one for backup and its configured on 30001 port and other is for restore/recovery on 30002 port.
The below diagram gives an idea about each steps

I’m using a new instance to demonstrate the backup and restore process.
- Lets start the instance 30001 a source for an entire example
>mongod –port 30001 –dbpath d:\data\TestRepSet_30001\ –replSet TestRepSet_30001 –oplogSize 128 –logpath d:\data\TestRepSet_30001.log
![]()
- Connect to an mongo instance using the port 30001
>mongo.exe –port 30001
- Configure single node replica set
> rsconf = { _id: “TestRepSet_30001”, members: [{ _id: 0, host: “localhost:30001” }] }
> rs.initiate( rsconf )
- Insert the dummy data
TestRepSet_30001:PRIMARY> for(var i=0;i<=100;i++) {
db.backupCollection.insert({“id”:+i, “Date”: new Date()}) }
- cross verify the count for our reference just to compare before and after restore
TestRepSet_30001:PRIMARY> db.backupCollection.count()

- Backup the database to specific path. You can also use default path. I’m using c:\data\backup

- Perform data manipulation(Insert and Delete few documents)
TestRepSet_30001:PRIMARY> for(var i=102;i<=1000;i++) { db.backupCollection.insert({“id”:+i, “Date”: new Date()}) }
TestRepSet_30001:PRIMARY> db.backupCollection.count()
TestRepSet_30001:PRIMARY> db.backupCollection.remove({“id” : {“$gt” :800}})
TestRepSet_30001:PRIMARY> db.backupCollection.count()

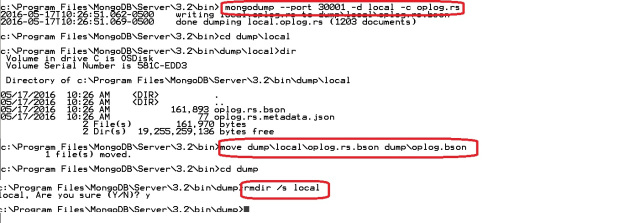
- Dump and move the oplog to default folder and remove the local folder
>mongodump –port 30001 -d local -c oplog.rs
>move dump\local\oplog.rs.bson dump\oplog.bson
>rmdir /s local
- Identify the time stamp for Point in time recovery
TestRepSet_30001:PRIMARY> db.oplog.rs.find({“ns”: “backup.backupCollection”,”op”:”d”}).sort({$natural:1}).limit(5)
![]()
- I have created an instance to restore the database. Have used 30002 port to demonstrate the restore process
>mongod –port 30002 –dbpath d:\data\TestRepSet_30002\ –logpath d:\data\TestRepSet_30002.log

- Restore the database from first snapshot from d:\data\backup to an instance hosted on 30002 port
>mongorestore –port 30002 d:\data\backup\

12. Connect to an instance to check the count
>mongo.exe –port 30002
>use backup
>db.backupCollection.count()
13. After you have the right time replay the logs
>mongorestore –port 30002 –oplogReplay –oplogLimit “1463498418:1”
14. Check the record count at the target database
 Job done
Job done
The learn other method you can refer the below link


