The following article shows, through code, how to enable SQL Agent alerts and
using a simple stored procedure and DLL, send emails via an SMTP server rather
than using SQL Mail. We will cover these items:
- SQL Agent Event Alerts
- SQL Agent Tokens
- Calling DLL's via sp_OA methods
- Using RAISEERROR
The SMTP DLL
Here is the code for our simplecdo DLL (some items have been cut to
make the code easier to read), the routine is coded in VB and makes use of the
standard CDO library:
Public Function SendMessage(ByVal
ToAddress As String, _
ByVal FromAddress As String, _
ByVal SubjectText As String, _
ByVal BodyText As String, _
ByVal Server As String, _
ByRef ErrorDescription As String) As Long
'This is the original function (no attachments).
'
Dim lngResult As Long
lngResult = Send(ToAddress, FromAddress, SubjectText,
BodyText, Server, "", ErrorDescription)
SendMessage = lngResult
End Function
Private Function Send(ByVal ToAddress As
String, _
ByVal FromAddress As String, _
ByVal SubjectText As String, _
ByVal BodyText As String, _
ByVal Server As String, _
ByVal AttachmentFileName As String, _
ByRef ErrorDescription As String)
'Simple function for sending email from an SQL Server stored
procedure.
'Returns 0 if OK and 1 if FAILED.
'
Dim Result As Long
Dim Configuration As CDO.Configuration
Dim Fields As ADODB.Fields
Dim Message As CDO.Message
On Error GoTo ERR_HANDLER
'Initialise variables.
Result = 0
ErrorDescription = ""
'Set the configuration.
Set Configuration = New CDO.Configuration
Set Fields = Configuration.Fields
With Fields
.Item(CDO.CdoConfiguration.cdoSMTPServer)
= Server
.Item(CDO.CdoConfiguration.cdoSMTPServerPort)
= 25
.Item(CDO.CdoConfiguration.cdoSendUsingMethod)
= CdoSendUsing.cdoSendUsingPort
.Item(CDO.CdoConfiguration.cdoSMTPAuthenticate)
= CdoProtocolsAuthentication.cdoAnonymous
.Update
End With
'Create the message.
Set Message = New CDO.Message
With Message
.To = ToAddress
.From = FromAddress
.Subject = SubjectText
.TextBody = BodyText
Set .Configuration = Configuration
'Send the message.
.Send
End With
EXIT_FUNCTION:
'Clean up objects.
Set Configuration = Nothing
Set Fields = Nothing
Set Message = Nothing
Send = Result
Exit Function
ERR_HANDLER:
Result = Err.Number
ErrorDescription = "Number [" &
Err.Number & "] Source [" & Err.Source & "] Description
[" & Err.Description & "]"
Me.LastErrorDescription =
ErrorDescription
GoTo EXIT_FUNCTION
End Function
Copy the compiled DLL to your DB server and run
the command below to install:
regsvr32 simplecdo.dll
The Stored Procedure
The routine below makes the simple call to the SMTP email DLL. We have
hard coded the IP (consider making it a parameter). I was also sloppy with
the subject heading for the email, again this should be a parameter or
better still a SQL Agent Token (see later).
CREATE PROCEDURE usp_sendmail
(@recipients varchar(200), @message varchar(2000)) AS
declare @object int, @hr int, @v_returnval varchar(1000), @serveraddress
varchar(1000)
set @serveraddress = '163.232.xxx.xxx'
exec @hr = sp_OACreate 'SimpleCDO.Message', @object OUT
exec @hr = sp_OAMethod @object, 'SendMessage', @v_returnval OUT, @recipients,
@recipients, 'test', @message, @serveraddress, @v_returnval
exec @hr = sp_OADestroy @object
GO
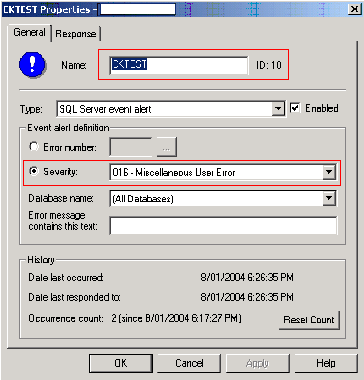
Creating the Alert
Run Enterprise Manager, under the Management folder expand SQL Agent and
right click Alerts - New Alert.
In this case our alert is called CKTEST, we are going to send the DBA
an email whenever a logged severity 16 message occurs for any databases (no
really practical, but this is just an example).
Click on the Response tab next.
Uncheck the email, pager and net send options (where applicable
for your system). Check the execute job checkbox, drop down the
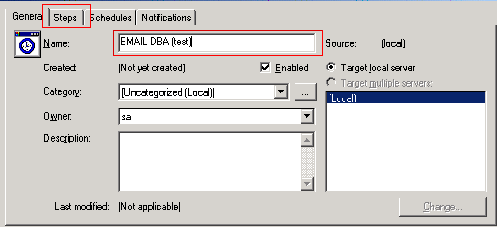
list box and scroll to the top, and select <New Job>.
Enter the Name of the new SQL Agent Job, then press the Steps button
to create a step that will call our stored procedure.
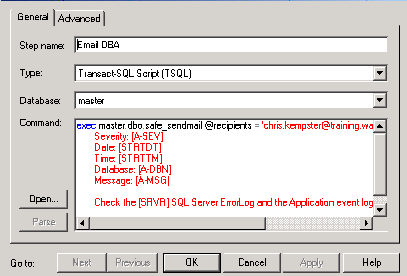
Here we enter the step name, it is a t-sql script of course, and the command
which is:
exec master.dbo.usp_sendmail @recipients
= 'support@chriskempster.com', @message = '
Error: [A-ERR]
Severity: [A-SEV]
Date: [STRTDT]
Time: [STRTTM]
Database: [A-DBN]
Message: [A-MSG]
Check the [SRVR] SQL Server ErrorLog and the Application event log on the
server for additional details'
This is where the power of Agent Tokens comes into play. The
tokens will be automatically filled in on the step running, there are
numerous tokens you can leverage off, but these are probably the best place to
start. Here are some examples:
[A-DBN] Alert
Database name
[A-SVR]
Alert Server name
[DATE]
Current Date
[TIME]
Current Time
[MACH]
Machine name
[SQLDIR] SQL Server root
directory
[STRTDT] Job start time
[STRTTM] Job end time
[LOGIN] SQL login
ID
[OSCMD] Command line prefix
[INST]
Instance name (blank if default instance)
Click OK twice and Job and its single step are now created. In the
Response windows press Apply, then press OK to exit the Alert creation
window and return back to enterprise manager.
Goto Jobs under SQL Server agent to confirm the new Job and its step we have
just created.
Testing the Alert
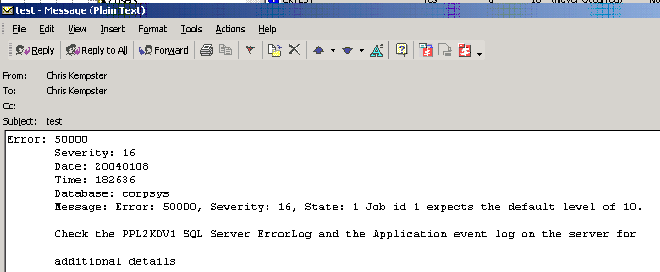
Run Query Analyser and run the following:
RAISERROR ('Job id 1 expects the
default level of 10.', 16, 1) with log
The with log clause is important, the alert will not fire
without it.
Shortly later I receive the following email:
Conclusion
The routines discussed provide an excellent basis for moving back to event
alerts if you have not already done so, all without the need for SQL Mail.
This provides you with a lot more flexibility, especially with the added
benefits of SQL Agent tokens, to really smarten up your daily monitoring.
References
VB Code for SMTP Routine, Donald Xie, 2001
"From SQLMail to SMTP in the SQL Agent", Bill Wunder, Published on
www.sswug.org, reference printed as at
8/1/2004.